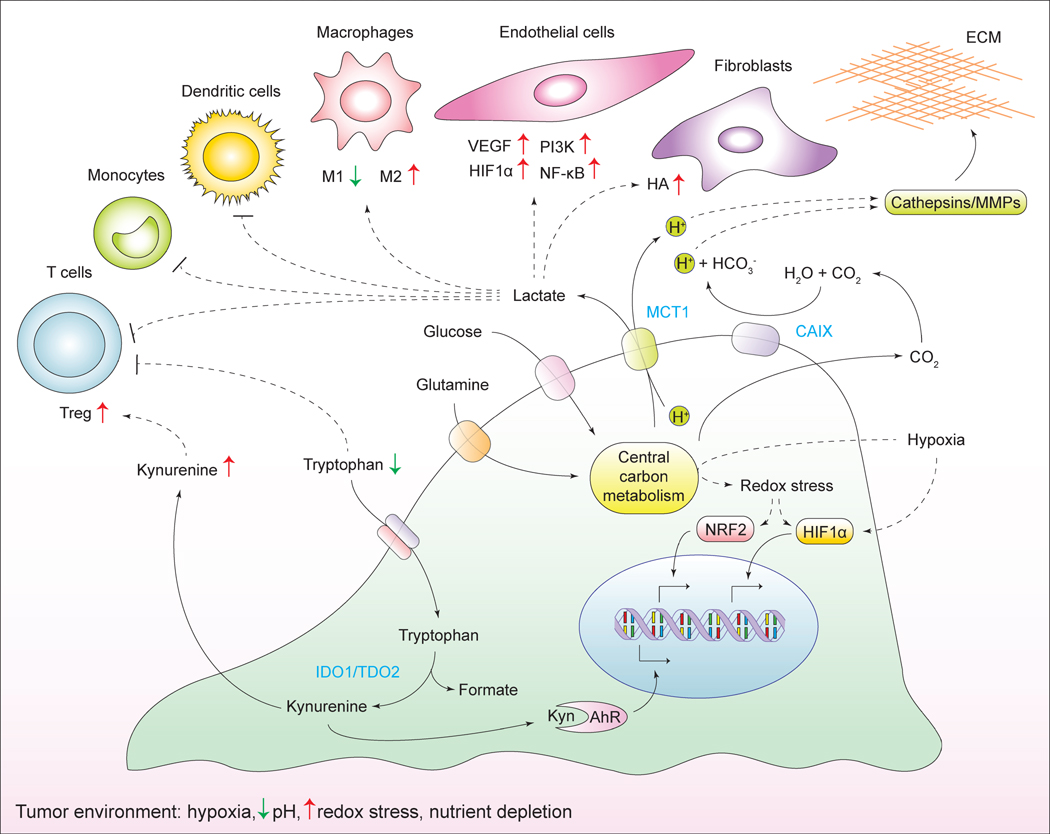
Figure 7. Metabolic interactions with the microenvironment.
Cancer cells alter the chemical composition of the extracellular milieu, which exerts pleiotropic effects on the phenotypes of normal cells that reside in the vicinity of the tumor, as well as the extracellular matrix. Reciprocally, the microenvironment affects the metabolism and signaling responses of cancer cells themselves. ECM, extracellular matrix; Treg, regulatory T cells; HA, hyaluronic acid; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; MCT1, monocarboxylate transporter 1; CAIX, carbonic anhydrase IX; IDO1, indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase 1; TDO2, tryptophan-2, 3-dioxygenase 2; Kyn, kynurenine; AhR, aryl -hydrocarbon receptor.