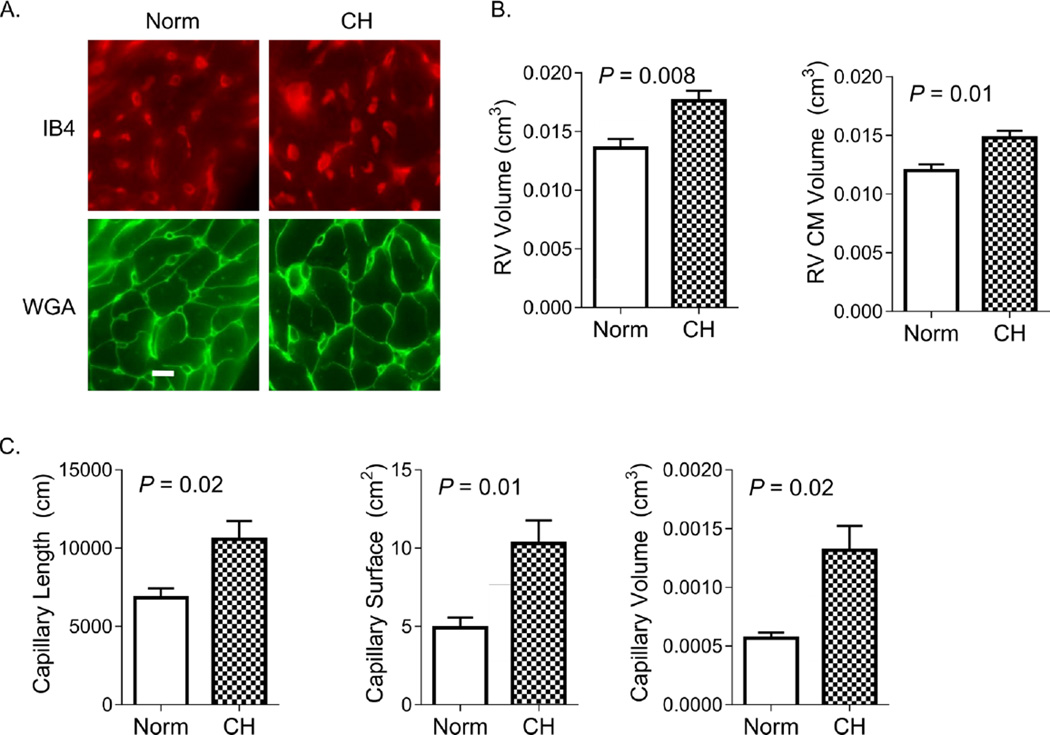
Figure 2. Chronic hypoxia induces early RV angiogenesis.
In (A), representative images of RV isotropic uniform random (IUR) sections stained with markers specific for endothelial cell glycoproteins (isolectin IB4) and myocyte plasma membrane glycoproteins (wheat germ agglutinin; WGA) are shown. IB4 stains endothelial cells of capillaries and larger resistance vessels, though only the former were quantified. Bar = 10 µm. Images were used for stereological assessment in animals exposed to normoxia (Norm) and chronic hypoxia (CH) for 7 days. In (B), RV volume and RV CM volume increase with CH. As shown in (C), RV capillary length, surface area, and luminal volume are significantly increased after 7 days of CH. P-values are for Student’s t-test.