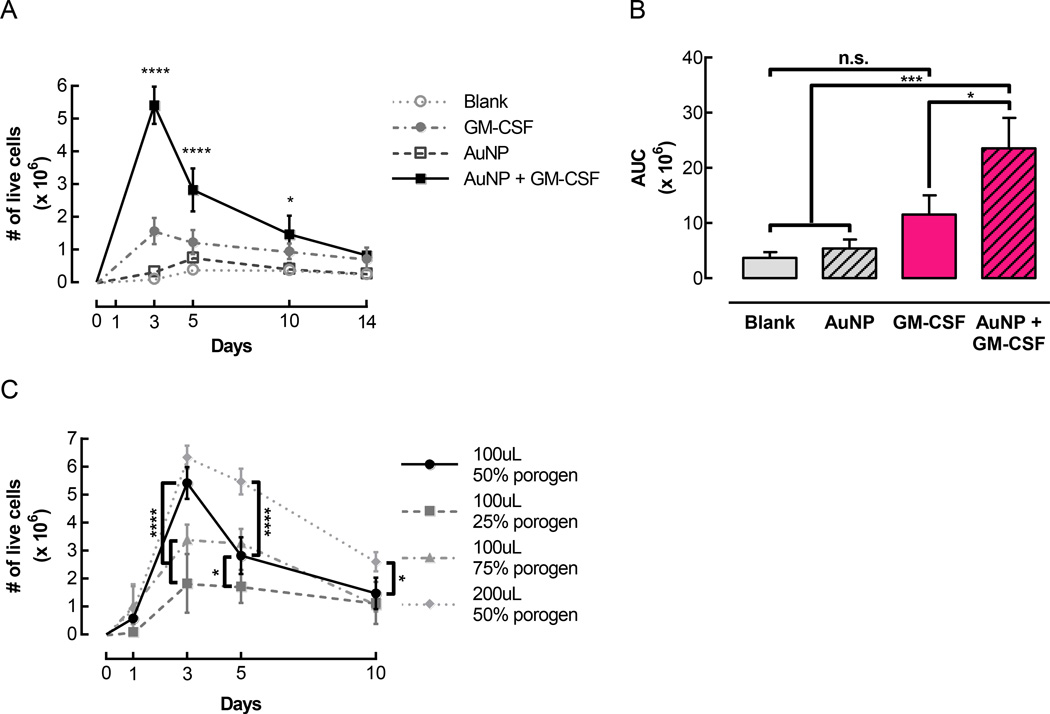
Figure 3.
Pore-forming gels delivering GM-CSF conjugated to AuNPs mediated substantial cell accumulation in vivo. Gels were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of C57BL/6J mice. At specified timepoints, gels were dissociated to retrieve and quantify infiltrating cells. (A) Number of live cells isolated over time from control gels (Blank and AuNP) and gels loaded with 3 µg GM-CSF either directly incorporated in the gels (GM-CSF) or first conjugated to AuNPs (AuNP + GM-CSF). For all conditions, pore-forming gels contained a 50% porogen volume fraction. (n = 3 – 9 per condition per timepoint; mean ± s.d. shown; * p < 0.05 compared to Blank and AuNP; **** p < 0.0001 compared to all other conditions; AuNP + GM-CSF condition was compared to all other conditions at each timepoint.) (B) Areas under curves corresponding to the data shown in (A). (* p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001; all conditions were compared to each other.) (C) The total volume and porogen volume fraction of pore-forming gels were varied, and infiltrating cells were quantified at specified timepoints. (n = 3 – 9 per condition per timepoint; mean ± s.d. shown; * p < 0.05; **** p < 0.0001; 100 µL 50% porogen condition was compared to all other conditions at each timepoint.)