Fig 7.
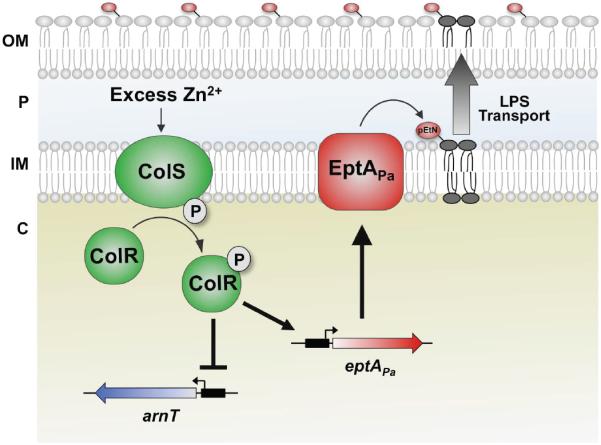
Proposed model of pEtN addition to P. aeruginosa lipid A. Upon sensing excess Zn2+, the ColS sensor kinase (green) autophosphorylates and transfers a phosphate group to the response regulator ColR (green). ColR then acts as a transcription factor, inducing transcription of eptAPa (red) while inhibiting that of arnT (blue). EptAPa protein is synthesized and transfers pEtN to the 4′-phosphate group of lipid A in the inner membrane. Lipid A is then transported to the bacterial cell surface. Following transport to the outer membrane, the 3-hydroxydecanoate acyl chain is removed by PagL (indicated in the model). In some instances, PagP can modify the lipid A (not shown). Cellular components are labelled as follows: OM, outer membrane; P, periplasm; IM, inner membrane; C, cytoplasm).
