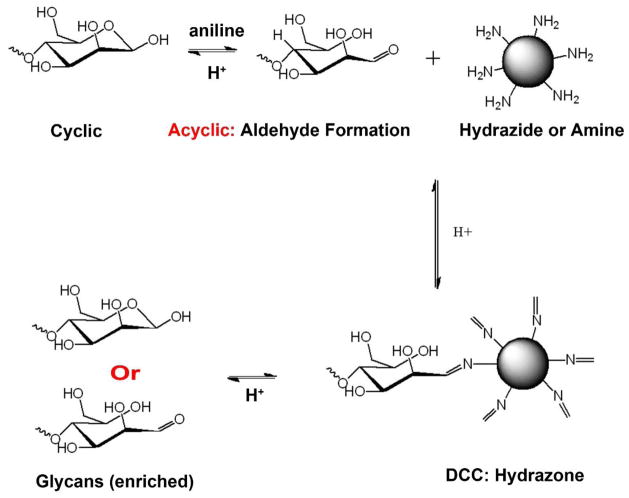
Figure 4. N-glycan enrichment and purification using reversible hydrazide chemistry.
N-glycans released by PNGase F are conjugated to beads functionalized with hydrazide groups. The hydrazides in acetic acid perform a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the acyclic reducing terminal residue of N-glycans to form a stable Schiff’s base conjugation (pH > 5.0). Aniline is added as a catalyst to quicken the reaction. After washing unbound molecules, N-glycans are released from beads via acidic hydrolysis (10% formic acid). This method allows for the enrichment and purification of N-glycans from biological samples. (Reprint with permission)