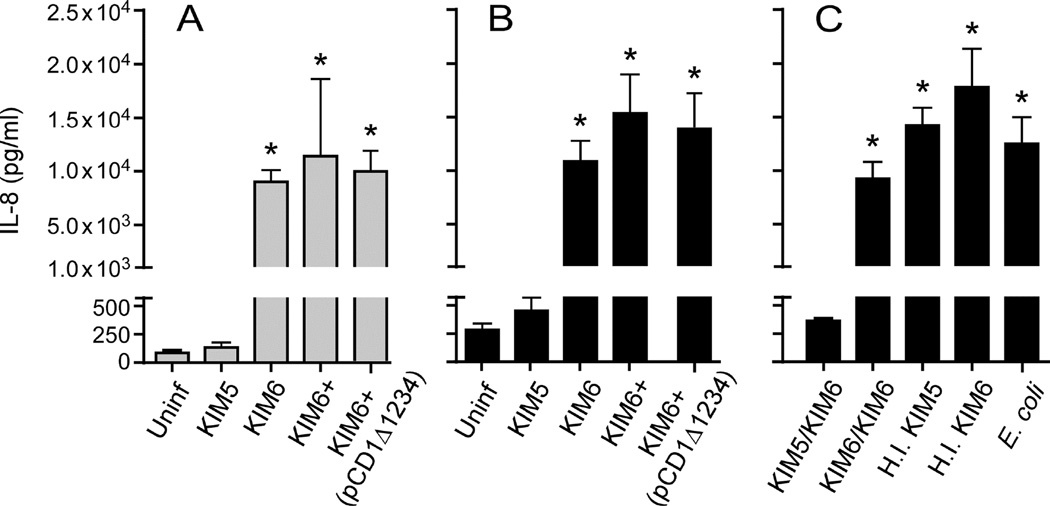
Fig. 2.
Y. pestis pCD1-dependent inhibition of IL-8 requires the effector Yop proteins. IL-8 secreted by human PMNs following incubation with Y. pestis containing the wild-type pCD1 virulence plasmid (KIM5), pCD1− Y. pestis with (KIM6+) or without (KIM6) the chromosomal Pgm locus, or with KIM6+ transformed with pCD1Δ1234 (which lacks the six effector Yop genes but encodes the genes necessary for the T3SS) were compared (A, B). Alternatively, PMNs were incubated with KIM5 or KIM6 prior to the addition of KIM6 (KIM5/KIM6 and KIM6/KIM6, respectively) or with heat inactivated (H.I.) KIM5 or KIM6 (C). PMNs incubated alone or with E. coli were included as controls. Culture supernatant was collected after 12 h (A) or 24 h (B, C) of incubation and the concentration of IL-8 was determined by ELISA. The mean and SEM for at least three independent experiments (except for H.I. KIM6 and E. coli, which were tested only twice) are indicated. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test. *, P < 0.05 compared to KIM5.