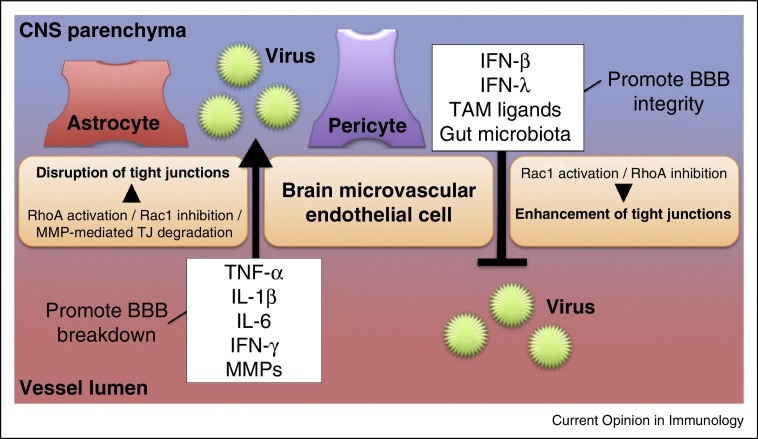
Figure 2.
Regulation of BBB integrity during viral infection. Pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IFN-γ, which are expressed either luminally or abluminally) act to open the BBB by causing breakdown of tight junctions. Astrocytes, pericytes, BMECs, leukocytes, and/or other cell types may produce these cytokines. MMPs disrupt BBB integrity during viral infection by directly degrading tight junctions. Collectively, the pro-inflammatory cytokines and MMPs facilitate viral crossing into the CNS parenchyma. By contrast, tight junction stabilization occurs in response to signals by type I IFNs (e.g., IFN-β) or type III IFN (IFN-λ). TAM receptor ligands induce signals that augment this effect by cooperating with type I IFN to activate Rac1, rearrange actin filaments, and stabilize endothelial tight junctions. Gut microbiota enhance BBB integrity as well, although its mechanistic role during neuroinvasive viral infection is yet to be defined.