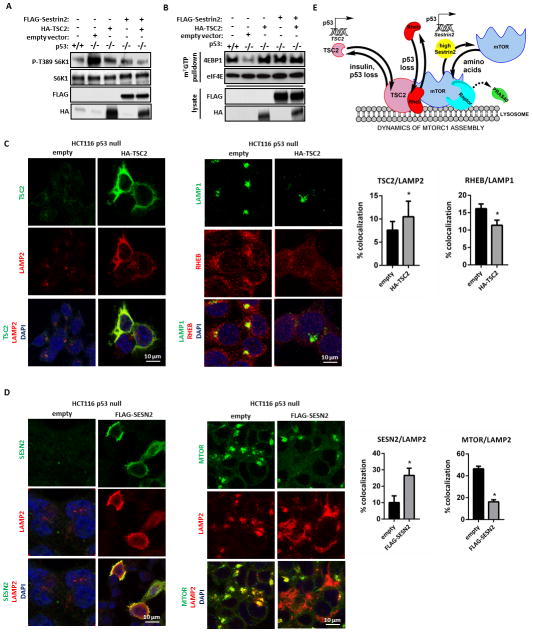
Figure 7. Forced expression of TSC2 and/or Sestrin2 decreases the elevated mTORC1 activity in p53 null cells down to levels seen in p53 wt cells.
(A) FLAG-tagged Sestrin2, HA-TSC2, or an empty vector control were transfected into p53−/− HCT116 cells, alone or in combination, and the degree of p-T389 S6K1 was visualized by immunoblotting. (B) Forced expression of TSC2 and/or Sestrin2 in p53 null cells increases m7GTP cap binding. m7GTP pulldown assays were performed on p53−/− HCT116 cells following transfection with the constructs in (A) and levels of bound 4EBP1 and eIF4E were detected by immunoblotting. (C) Transfection of HA-TSC2 into HCT116 cells null for p53 restores lysosomal TSC2 and diminishes Rheb at lysosomal membranes. The increase in lysosomal TSC2 and decrease in lysosomal Rheb were statistically significant (p= 0.024 and 0.036, respectively, n = 40). (D) Transfection of Flag-Sestrin2 into HCT116 cells null for p53 decreases partitioning of mTOR to the lysosome. The distribution of both Sestrin2 (SESN2) and of mTOR to the lysosome was significantly different after transfection (p<0.01 (n = 40) and < 0.0001 (n = 60), respectively). TSC2 localizations to the lysosomes in these cell populations were not significantly different (Fig. S3). (E) Proposed mechanism of p53 involvement in control of mTORC1. In cells with basal wt p53 function, p53-dependent transcription supplies adequate levels of TSC2 and sestrin2 to regulate mTORC1 kinase activity; when cells lose p53 transcriptional activity, TSC2 and Sestrin2 levels are low, TSC2 binding at the lysosomal sites of mTORC1 is low, Rheb levels are higher at these sites, and PRAS40 is lower in mTORC1 complexes, enhancing mTORC1 activity. When Sestrin2 is high, as after transfection, the distribution of mTOR to the lysosome is dramatically decreased. When Sestrin2 is decreased from unstressed steady state levels, due to loss or mutation of p53, the distribution of mTOR onto lysosomal membranes is unchanged. In p53 deficient cells the association of lysosomal mTOR with Raptor is increased, an effect that also increases mTORC1 activity, but it remains unclear whether Sestrin2 levels play a role in this effect.