Abstract
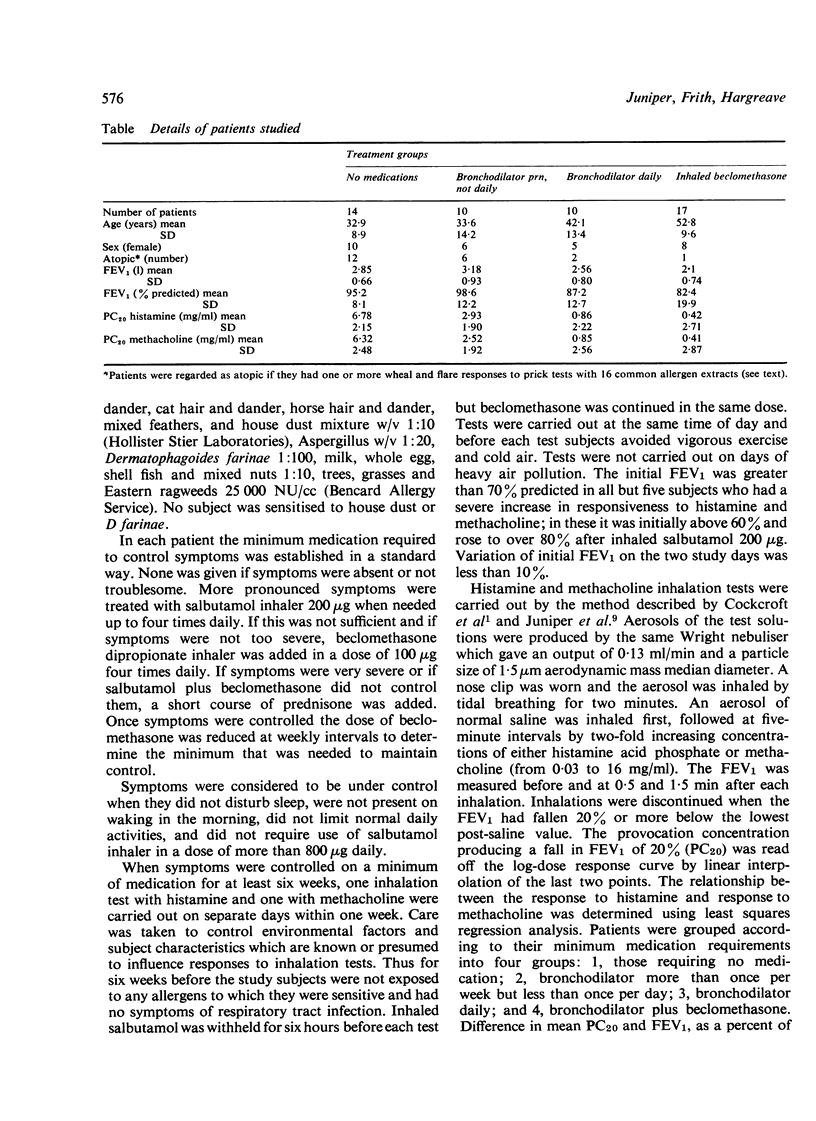
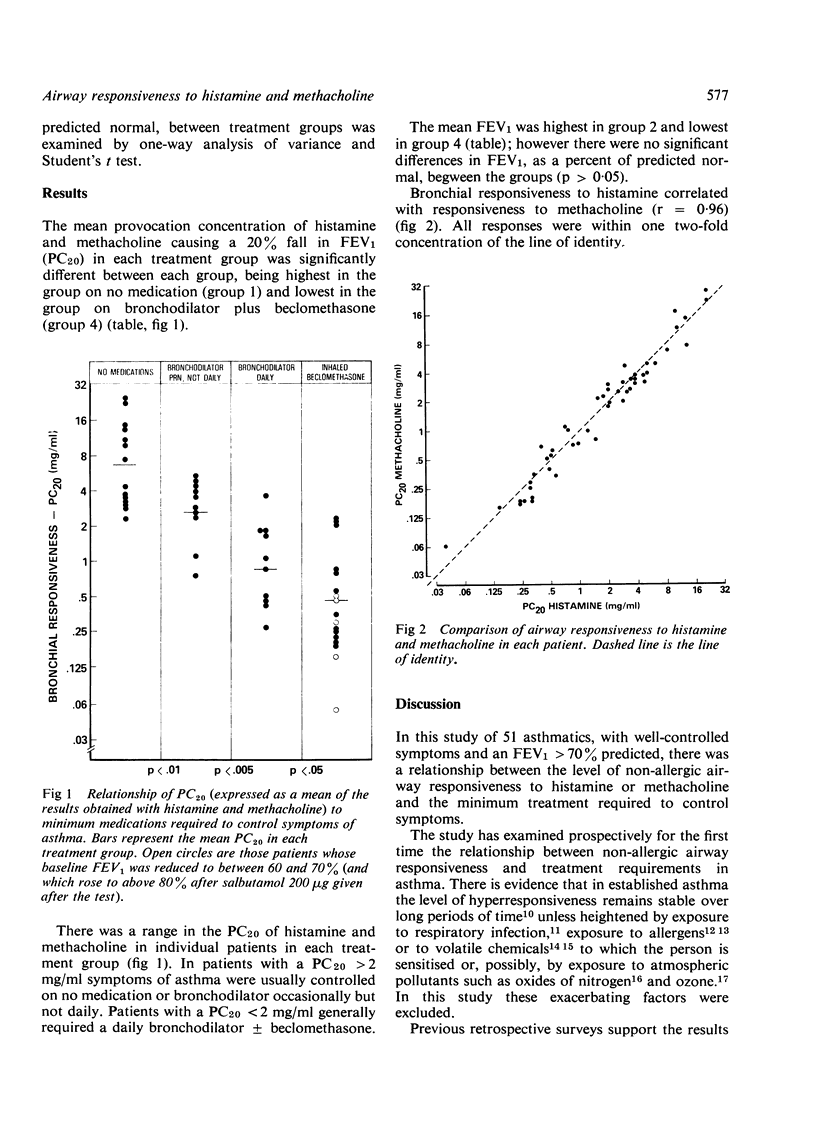
We have prospectively examined in 51 patients the relationship between the level of airway responsiveness to histamine and methacholine and the minimum medications required to control asthma. First we determined the least medication that was required to control symptoms so that they did not disturb sleep, were not present on waking, and did not require use of inhaled salbutamol (200 microgram) more than four times daily. When baseline FEV1 was greater than 70% of predicted and when there had been no respiratory infection or allergen exposure for six weeks, histamine and methacholine inhalation tests were carried out on separate days to determine the provocation concentration causing a fall in FEV1 of 20% (PC20). There was a close correlation between the PC20 to the two agents. The patients were grouped into 1, those who required no medication; 2, those who required salbutamol (200 microgram) occasionally but not daily; 3, those who required daily salbutamol; and 4, those who required additional beclomethasone dipropionate. The mean PC20 was highest in group 1 and lowest in group 4; there was a significant difference between each group. The results indicate that airway responsiveness to vasoactive amines is either an important determinant of the severity of asthma and the medication requirements or a consequence of the severity of asthma. They raise the possibility that measurement of responsiveness may be useful in some patients with established asthma to substantiate or question medication needs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cockcroft D. W., Cotton D. J., Mink J. T. Nonspecific bronchial hyperreactivity after exposure to Western Red Cedar. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Mar;119(3):505–510. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.3.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Killian D. N., Mellon J. J., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine: a method and clinical survey. Clin Allergy. 1977 May;7(3):235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1977.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Ruffin R. E., Dolovich J., Hargreave F. E. Allergen-induced increase in non-allergic bronchial reactivity. Clin Allergy. 1977 Nov;7(6):503–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1977.tb01481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Ruffin R. E., Frith P. A., Cartier A., Juniper E. F., Dolovich J., Hargreave F. E. Determinants of allergen-induced asthma: dose of allergen, circulating IgE antibody concentration, and bronchial responsiveness to inhaled histamine. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Nov;120(5):1053–1058. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.5.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggleston P. A. A comparison of the asthmatic response to methacholine and exercise. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Feb;63(2):104–110. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90199-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. A., Nadel J. A., Boushey H. A. Bronchial hyperirritability in healthy subjects after exposure to ozone. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Aug;118(2):287–294. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton D. J., Suda W. L., Kinsman R. A., Souhrada J., Spector S. L. Bronchoconstrictive suggestion in asthma: a role for airways hyperreactivity and emotions. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jun;117(6):1029–1038. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.6.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juniper E. F., Frith P. A., Dunnett C., Cockcroft D. W., Hargreave F. E. Reproducibility and comparison of responses to inhaled histamine and methacholine. Thorax. 1978 Dec;33(6):705–710. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.6.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam S., Wong R., Yeung M. Nonspecific bronchial reactivity in occupational asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Jan;63(1):28–34. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Hall W. J., Douglas R. G., Jr, Mudholkar G. S., Speers D. M., Patel K. Airway hyperreactivity and peripheral airway dysfunction in influenza A infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Aug;118(2):295–303. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.2.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S. Clinical significance of bronchial sensitivity to acetylcholine and histamine in bronchial asthma. J Allergy. 1966 Sep;38(3):127–142. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(66)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orehek J., Massari J. P., Gayrard P., Grimaud C., Charpin J. Effect of short-term, low-level nitrogen dioxide exposure on bronchial sensitivity of asthmatic patients. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):301–307. doi: 10.1172/JCI108281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinfeld A. R., Pain M. C. Perception of asthma. Lancet. 1976 Apr 24;1(7965):882–884. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shim C. S., Williams M. H., Jr Evaluation of the severity of asthma: patients versus physicians. Am J Med. 1980 Jan;68(1):11–13. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. L., Farr R. S. A comparison of methacholine and histamine inhalations in asthmatics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Oct;56(4):308–316. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townley R. G., Ryo U. Y., Kolotkin B. M., Kang B. Bronchial sensitivity to methacholine in current and former asthmatic and allergic rhinitis patients and control subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Dec;56(6):429–442. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


