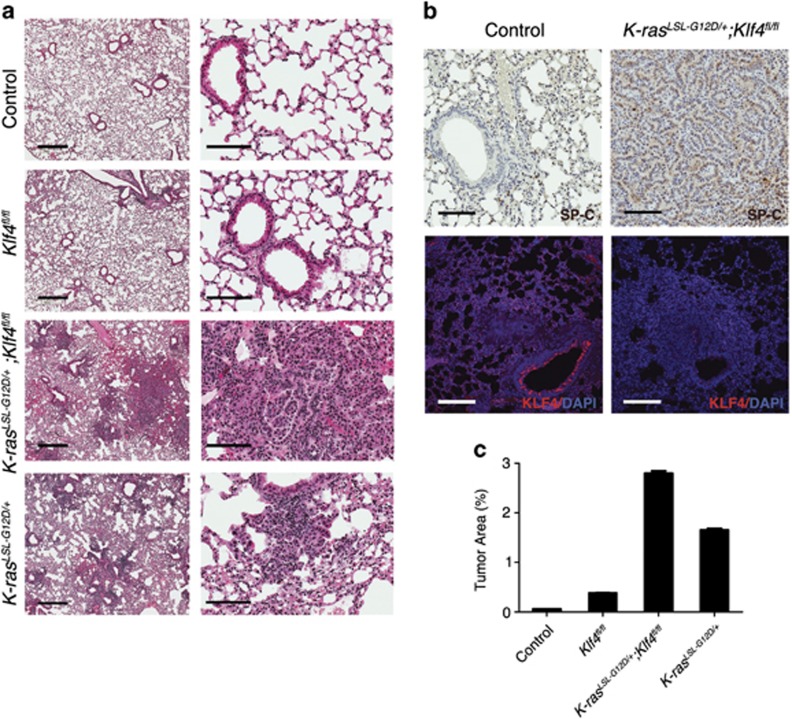
Figure 4.
Klf4 deletion facilitates lung tumor formation and progression. (a) H&E staining of the lung tissue from wild-type mice (control), the K-rasLSL-G12D/+mice, Klf4fl/fl mice and K-rasLSL-G12D/+;Klf4fl/fl mice by 8 weeks post infection. Scale bars from left to right: 2 mm and 100 μm. (b) IHC staining of SP-C (top) and immunofluorescent staining of KLF4 (red, bottom) showing that SP-C tends to increase in tumor tissue from K-rasLSL-G12D/+;Klf4fl/fl mice than in normal tissue from wild-type mice. Scale bars: 100 μm. (c) Statistical analysis of the percentage of tumor area by 8 weeks post infection (based on H&E staining). Data are represented as mean±S.D