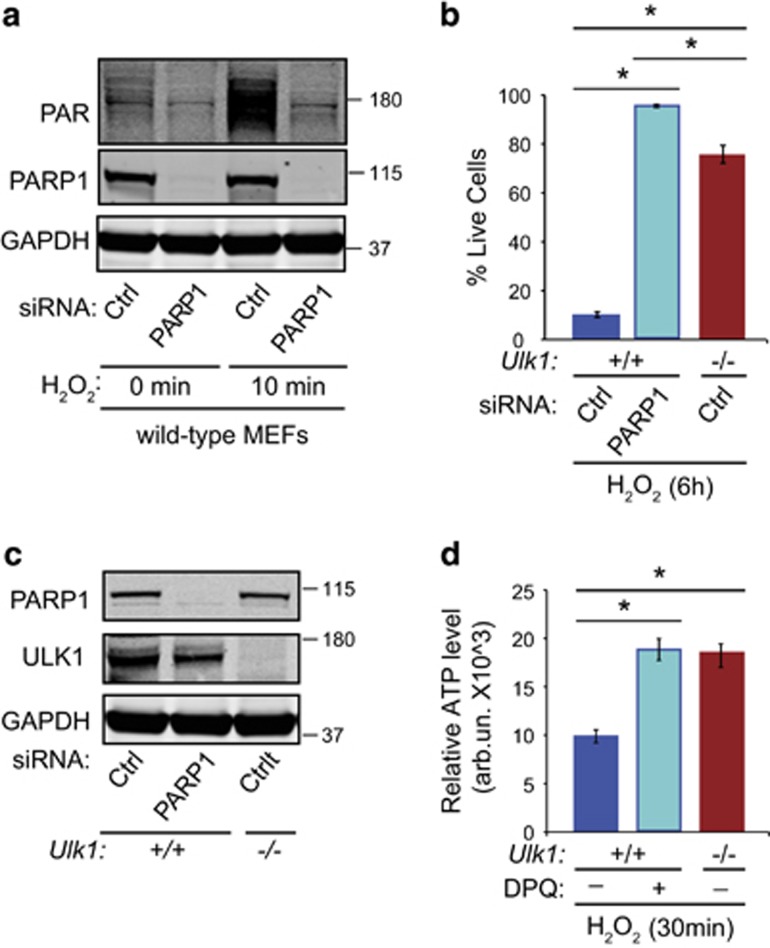
Figure 4.
PARP1 is a major source of PAR formation and cell death. (a) WT MEFs transfected with nontargeting (Ctrl) or PARP1 siRNA for 48 h were treated with 500 μM H2O2 for 10 min. PARP activation was measured by immunoblot analyses using an anti-PAR antibody. PAR-polymer formation was decreased with PARP1 knockdown. (b) WT MEFs transfected with nontargeting (Ctrl) or PARP1 siRNA and Ulk1−/− MEFs transfected with Ctrl siRNA were treated with 500 μM H2O2 for 6 h. The percentage of live cells was determined by performing the trypan blue-exclusion assay. The protection conferred by the lack of ULK1 in MEFs was comparable to that after PARP1 silencing. (c) Immunoblot analyses demonstrate the efficiency of PARP1 knockdown in WT MEFs. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (d) ATP levels were measured in WT or Ulk1−/− MEFs treated with H2O2 in the presence or the absence of 40 nM 3,4-dihydro-5[4-(1-piperindinyl)butoxy]-1(2H)-isoquinoline (DPQ), as indicated. The experiments were performed in triplicate. *P<0.001