Figure 3. γδT17 Cells Are Activated by Inf-DCs via IL-23.
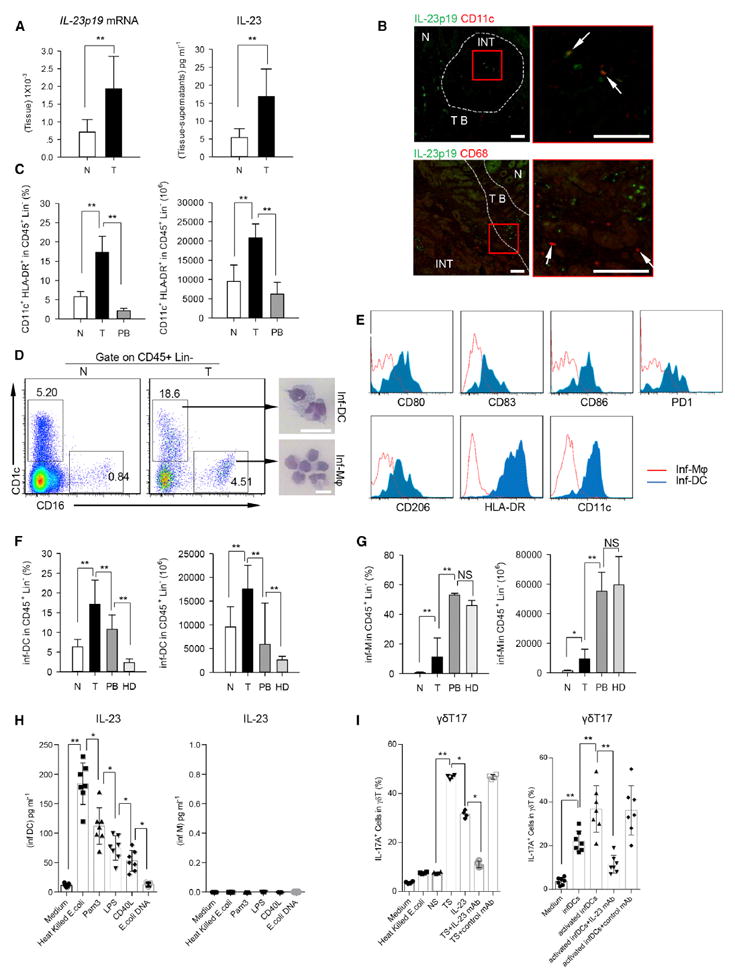
(A) Left panel shows that the relative mRNA level of IL-23p19 in tumor and paired normal tissues was determined by quantitative RT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH. Right panel shows concentrations of IL-23 in tumor and paired normal tissue-derived supernatants were detected by ELISA. N, normal tissue; T, tumor. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 5; **p < 0.01.
(B) Left panel shows representative images of paraffin sections from CRC patients stained with anti-human IL-23p19 (green) and anti-human CD11c (upper, red) or anti-human CD68 (lower, red) by IF staining (scale bars represent 100 μM). Right panel represents magnified view indicated by the red box in the left panel (scale bars represent 100 μM). The arrows indicate colocalizations of CD11c and IL-23p19 intumor (upper), but not for CD68 and IL-23p19 (lower). One of three independent experiments is shown. N, normal tissue; TB, tumor border; INT, intratumor.
(C) Percentages (in CD45+ Lin− cells) and absolute numbers (in 1 × 106 CD45+ Lin− cells) of CD11c+ HLA-DR+ cells in normal tissues, paired tumor, and autologous PB were quantified by FCM. N, normal tissue; T, tumor; PB, peripheral blood. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 20; **p < 0.01.
(D) Left panel shows representative flow cytometric analysis of inf-DCs (CD45+ Lin− CD1c+ CD16−) and inf-macrophages (CD45+ Lin− CD1c− CD16+) in tumor and paired normal tissues from CRC patients. Plots were gated on CD45+ Lin− cells. One of ten independent experiments is shown. Right panel shows Giemsa/May-Grunwald staining that shows morphology of tumor-infiltrating inf-DCs and inf-macrophages (scale bars represent 20 μM) sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). One of six independent experiments is shown. N, normal tissue; T, tumor.
(E) Phenotypes of tumor-infiltrating inf-DCs (CD45+ Lin− CD11c+ HLA-DR+ CD1c+ CD16−) and inf-macrophages (CD45+ Lin− CD11c+ HLA-DR+ CD1c− CD16+) were detected by FCM. One of three independent experiments is shown.
(F) Percentages and absolute numbers (in 1 × 106 CD45+ Lin− cells) of inf-DCs in tumor, paired normal tissues, autologous PB and PB from healthy donors were quantified by FCM. N, normal tissue; T, tumor; PB, peripheral blood; HD, healthy donors. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 20; **p < 0.01.
(G) Percentages and absolute numbers (in 1 × 106 CD45+ Lin− cells) of inf-macrophages in the same set of samples as in above (F) were quantified by FCM. N, normal tissue; T, tumor; PB, peripheral blood; HD, healthy donors. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 20; NS, no statistical significance; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
(H) Sorted tumor-infiltrating inf-DCs (left) and inf-macrophages (right) were treated with various ligands (heat-killed E. coli, Pam3, LPS, CD40L, E.coli DNA or Medium alone) for three days in vitro. IL-23 levels in the supernatants were detected by ELISA. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 6; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
(I) Left panel shows that γδT cells sorted from normal tissues were treated with heat-killed E.coli, NS, TS, IL-23, TS with IL-23 neutralizing antibody or TS with control mAb respectively for 14 days. Right panel shows that the sorted γδT cells were cocultured with resting inf-DCs or pre-activated inf-DCs (treated with heat-killed E. coli for three days) sorted from paired tumor tissues in the medium containing IL-23 neutralizing antibody or not for 2 weeks in vitro. Percentages of IL-17A+ cells in γδT cells were determined by FCM. NS, normal tissue-derived supernatants; TS, tumor-derived supernatants. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 6; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
See also Figures S3 and S4.
