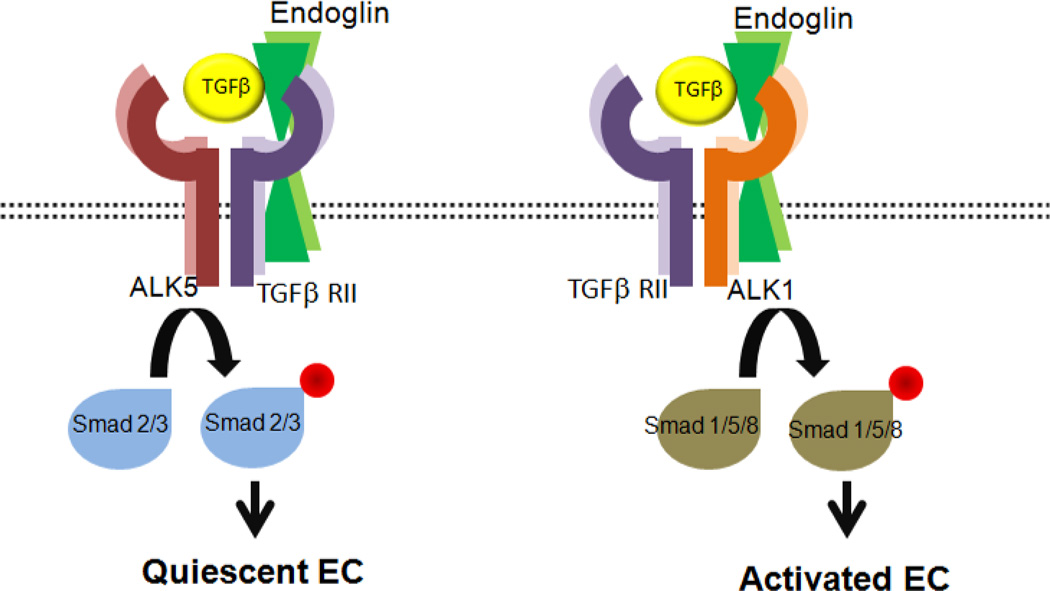
Figure 7. The proposed role of endoglin in TGFβ signaling pathways.
TGFβ bound TGFβRII recruits TGFβRI (ALK5 or ALK1), forms a heteromeric complex, and phosphorylates TGFβRI. The phosphorylated ALK5 and ALK1 phosphorylate Smad 2/3 and Smad 1/5/8, respectively. Activated Smad2/3 promotes the quiescence of EC, while activated Smad 1/5/8 promote EC proliferation and migration. Endoglin is phosphorylated by TGFβRII and ALK5/ALK1 complex and phosphorylated endoglin by ALK1 modulates ALK1 dependent EC growth and adhesion [185]. In addition, endoglin participate in none-cananical signaling pathways such as MAPK pathways. Our recent studies showed that appropriate expression of endoglin in EC is essential for attenuation of MAPK/ERKs pathway and regulation of their angiogenic properties [185].