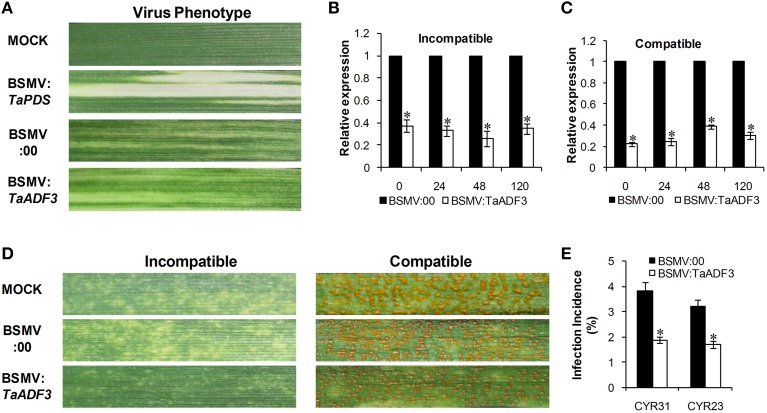
Figure 6.
Functional characterization of TaADF3 during interaction of wheat and Pst by BSMV-mediated gene silencing. (A) Photobleaching was evident on the fourth leaves of wheat plants inoculated with BSMV:TaPDS. Mild chlorotic virus symptoms were observed on the fourth leaves of wheat seedlings inoculated with BSMV:00 or BSMV:TaADF3. MOCK: wheat leaves inoculated with FES buffer. Silencing efficiency of TaADF3 in the fourth leaves of TaADF3-knockdown plants in incompatible (B) or compatible (C) interaction. Wheat leaves inoculated with BSMV:00 and further challenged by stripe rust fungus were used as the controls. The data were normalized to the TaEF-1α gene. (D) Disease phenotypes of the fourth leaves further challenged by avirulent CYR23 or virulent CYR31. Photos were taken 14 days post pathogen inoculation. (E) Silencing of TaADF3 attenuated infection of the virulent Pst CYR31 and the avirulent Pst CYR23. Only infection sites where substomatal vesicle formed were considered as successful penetration. The number of successful infection sites per 100 stoma was calculated. Three independent biological replications were performed, and 20 sets of infection incidence were measured for each biological replication. Asterisks indicate a significant difference (P < 0.05) from BSMV:00 using Student's t-test.