Figure 1. Factors associated with Pol I transcription and mRNA translation.
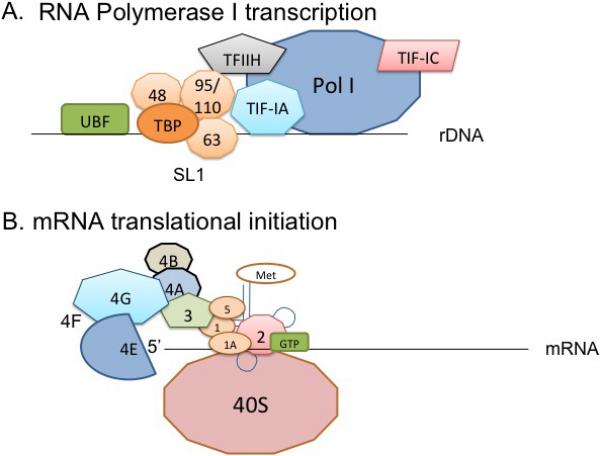
(A) Transcription of rDNA by RNA polymerase I (Pol I). Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is transcribed from rDNA by Pol I and its associated factors. A pre-initiation complex of Pol I, upstream binding factor (UBF), and the SL1 complex forms around rDNA. The SL1 complex consists of the TATA-binding protein (TBP) and three Pol I specific TBP-associated factors (TAFs): TAFI48, TAFI63, and TAFI95/110. Transcription intermediary factor IA (TIF-IA), TIFIC, and transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) also assist in rDNA transcription. (B) Cap-dependent mRNA translation initiation. A ternary complex of initiator met-tRNA, eIF2, and GTP becomes part of the larger 43S pre-initiation complex by associating with the 40S small ribosomal subunit, eIF1, eIF1A, and eIF3. eIF3 binds to eIF4G in the eIF4F complex to recognize mRNA. The eIF4F complex comprises of eIF4E, eIF4G, and eIF4A. eIF4E recognizes the 5’ 7-methyl-guanosine cap, eIF4A performs RNA helicase activity on mRNA, and eIF4G binds to the poly(A)-binding protein (PABP) (not shown) and the 43S pre-initiation complex via eIF3. eIF4F is stabilized by eIF4B. eIF5 is recruited to trigger joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit once the mRNA start codon is recognized.
