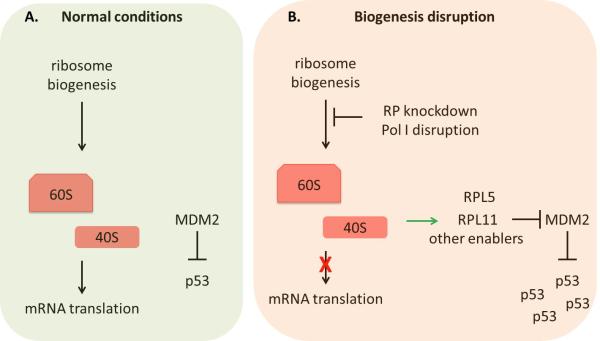
Figure 5. Targeting ribosome biogenesis.
(A) Under normal conditions cells produce 60S and 40S ribosomal subunits through ribosome biogenesis in order to translate mRNA into protein. In addition, p53 is targeted for degradation by the E3 ubiquitin ligase MDM2. (B) Disruption of ribosome biogenesis, whether from ribosomal protein (RP) knockdown or from RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) disruption, causes cells to slow or stop the production of fully functional ribosomal subunits, which impairs mRNA translation. Furthermore, disruption of ribosomal protein production causes enabler RPs to bind to MDM2 inhibiting p53 ubiquitination. This stabilizes p53 leading to cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, or senescence.