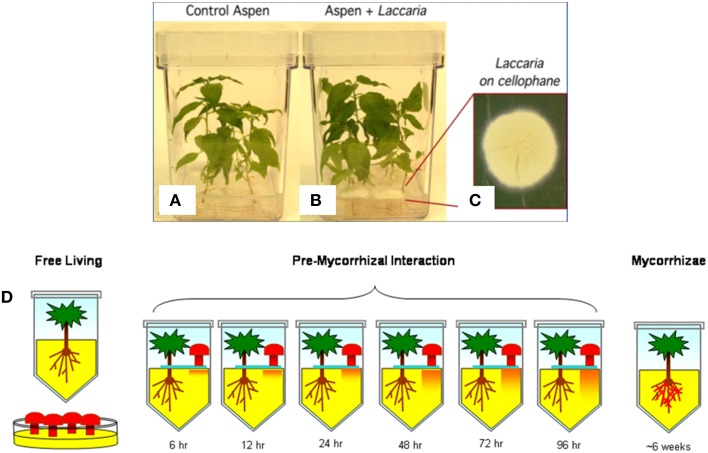
Figure 3.
Outline of biological system experimental design. A typical example of laboratory aspen and Laccaria interaction cultures are pictured. (A) Aspen seedlings grown in monoculture. (B) Aspen and Laccaria grown in co-culture after 96 h. In this co-culture condition, Laccaria mycelia are cultured on a membrane (C) and transplanted onto surface of aspen seedling cultures, as in (B). The separating membrane permits exchange of diffusible signaling molecules between aspen roots and Laccaria mycelia, but prevents physical contact between organisms. There were a total of nine experimental conditions that ranges from free-living aspen seedling and Laccaria mycelium, to co-cultured but physically separated by a permeable membrane to fully formed mycorrhizae (D). In the cartoon, while Laccaria is symbolized by mushroom shapes, no fruiting bodies were actually present in experimental design.