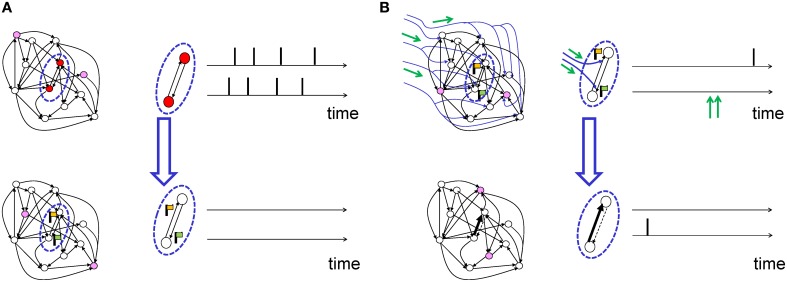
Figure 4.
Schematic of eligibility traces. (A) Joint activity (top) of two neurons (red-filled circles mark active neurons, open circles inactive neurons) leads, a few moments later (bottom), to the raising of a “flag” at synapses connecting those two neurons. These synapses are now eligible for change. The activity of other neurons (filled pink circles) does not interfere with the flag, which persists over a short time. (B) Axonal branches of dopaminergic neurons are shown in blue. If a neuromodulatory signal (green arrows, top) arrives, the synapses with raised flags undergo plasticity (top: synapses of medium strength before phasic neuromodulatory signal; bottom: synapses after change). Bottom: In a model where the amplitude of STDP is amplified by the neuromodulator, a synapse becomes stronger (bold arrow) in case of earlier pre-before-post spike timing and weaker (dashed arrow) in case of reversed timing. Synapses remain stable thereafter.