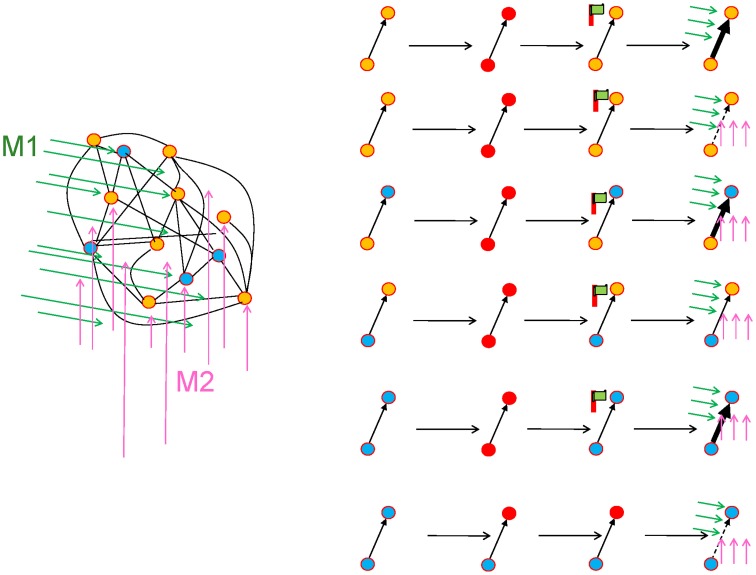
Figure 6.
Specificity of synaptic changes (schematic). In a network with several neuron types (here two types, orange and blue filled circles) and several neuromodulators (green arrows for neuromodulator M1 and magenta for M2), synaptic changes can be highly specific, even if phasic signals of neuromodulators have broad and unspecific target regions. Hypothetical examples, from top to bottom (red = active neuron): A connection from orange to orange becomes stronger (bold arrow), if both neurons and neuromodulator M1 are active; the same connection becomes weaker (dashed arrow), if in addition M2 is active; a connection from orange to blue is strengthened if both neurons and both neuromodulators are active; in the same situation, a connection from blue to orange is not affected; a connection from blue to blue is strengthened if both neurons and both neuromodulators are active; the same connection becomes weaker if only the postsynaptic neuron is active.