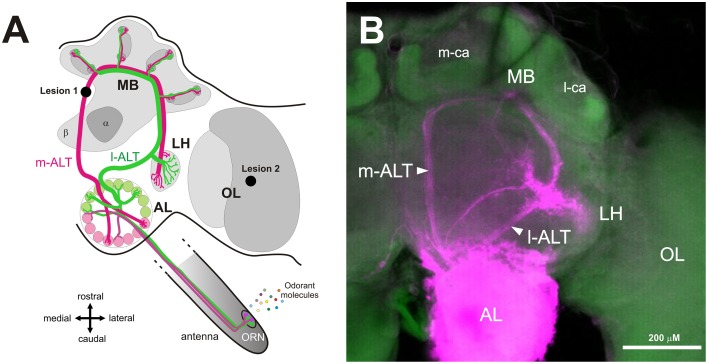
Figure 1.
Dual olfactory pathway of the honey bee brain. (A) Schematic overview of the dual olfactory pathway of the honey bee brain (adapted from Carcaud et al., 2012, 2015). Odorant molecules are detected by olfactory receptor neurons (ORN) on the antenna which project to the antennal lobe (AL). Then, projection neurons (PN) convey information to the mushroom bodies (MB) and the lateral horn (LH) via two main tracts, the medial antennal lobe tract (m-ALT, magenta) and the lateral antennal lobe tract (l-ALT, green). Lesion site of the m-ALT and of the optic lobe (OL) are indicated (lesion 1 and lesion 2 respectively). (B) Mass staining in the AL, showing the course of l-ALT and m-ALT PNs from the AL to LH and the MB calyces. Abbreviations: m-ca, median calyx; l-ca, lateral calyx.