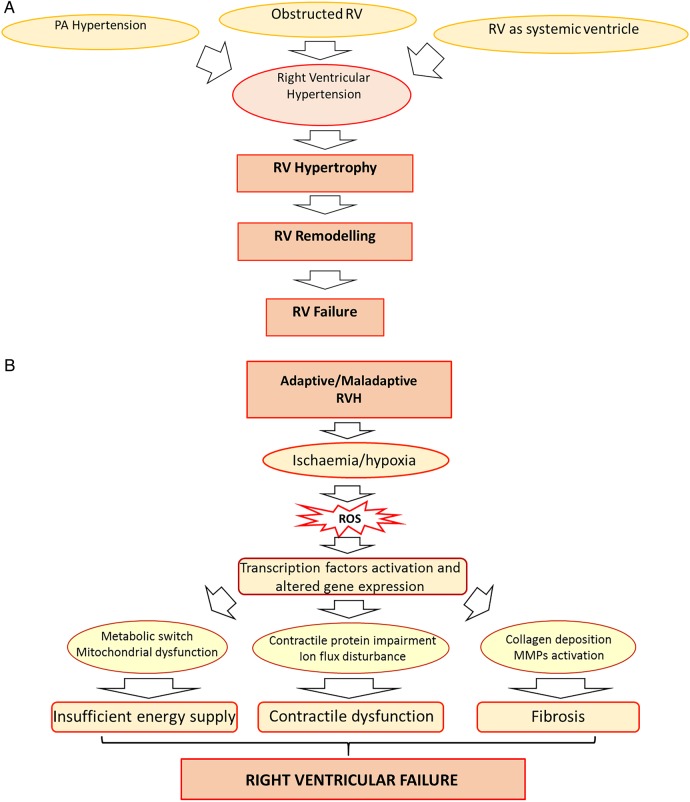
Figure 1.
(A) An overview of changes associated with RV pressure overload. Key triggers of RV pressure overload include pulmonary hypertension, RV outflow tract obstruction or RV being the systemic ventricle. RV pressure overload induces RVH that, through remodelling, leads to RV failure. It is of note, however, that RV failure is a continuous process and may begin as the time of hypertrophy and remodelling rather than being seen as a sequential process. (B) Effect of RVH-induced ischaemia. RVH is characterised by tissue hypoxia arising from ischaemia and microcirculatory insufficiency. Ischaemia-derived ROS, through the activation of transcription factors, drive the metabolic remodelling, contractile dysfunction and fibrosis that occur in RV failure. RVH, RV hypertrophy; PA, pulmonary artery; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases.