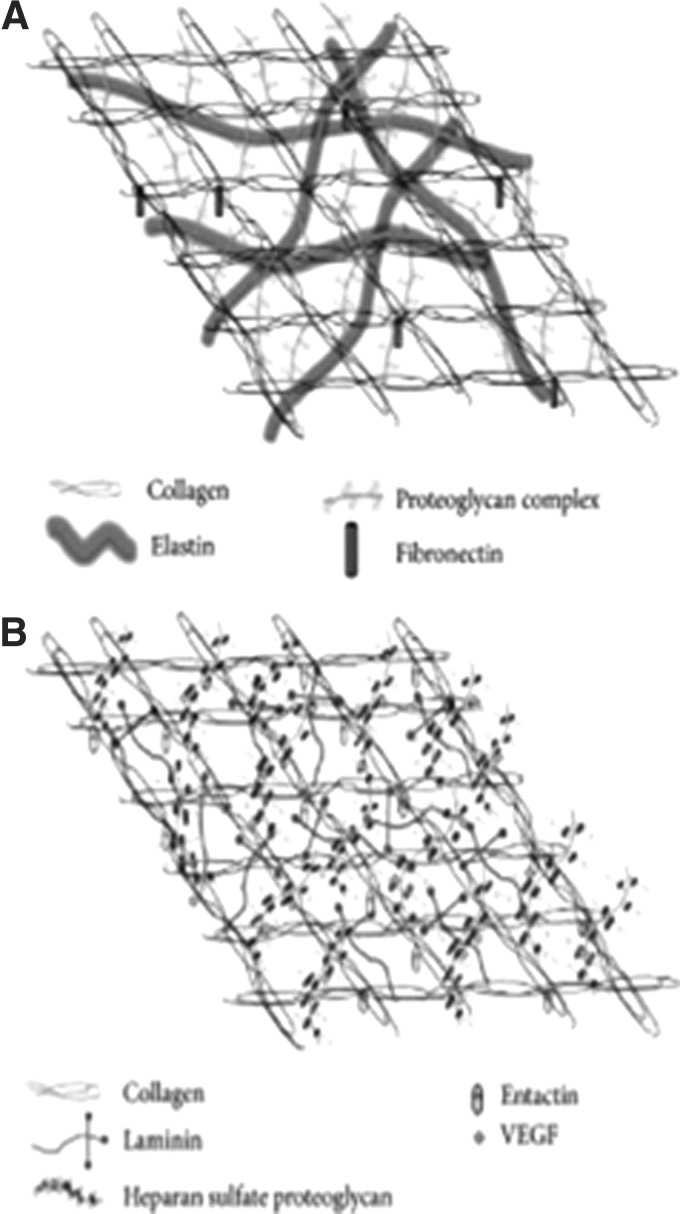
Figure 2.
ECM interactions and molecular organization. The ECM is composed of two distinct matrix entities. The protein composition of each leads to identifiable structural and functional differences; however, the two components interact to provide adhesive and structural support as well as influence cellular physiologic function. (A) The interstitial matrix, composed of fibrillar and nonfibrillar collagen, elastic fibers, and glycosaminoglycans, forms an amorphous structure that provides a repository for bioactive molecules. (B) With its high content of collagen IV, laminins, and heparin sulfate proteoglycans, the extracellular BM forms sheets that separate cells from the interstitial matrix (reprinted under CC BY license, Neve et al.16). BM, basement membrane; ECM, extracellular matrix.