Fig. 4.
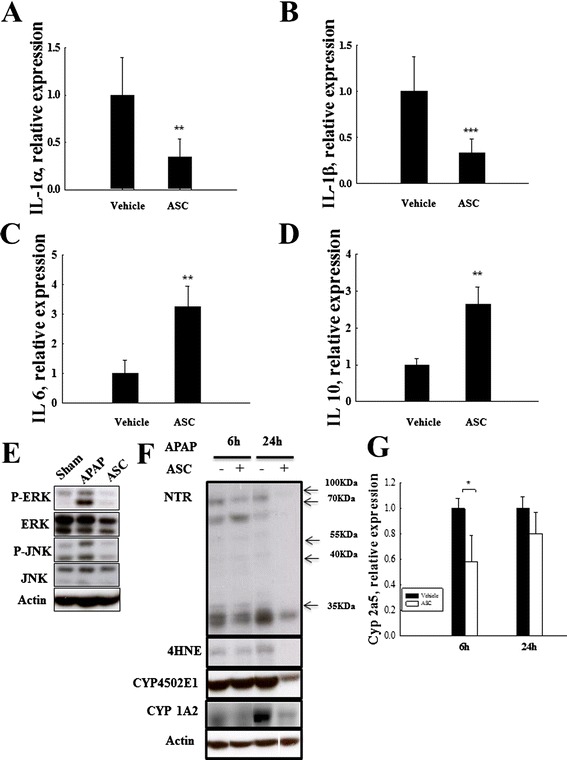
Omentum-derived ASC transplantation attenuated APAP-induced inflammation, and MAPK signaling activation. Omentum-derived ASC transplantation decreased the expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines (a) IL-1α and (b) IL-1β and increased the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines (c) IL-6 and (d) IL-10 to a significant degree. Omentum-derived ASC transplantation suppressed the MAPK signaling pathway activation induced by APAP treatment. e Liver tissue was collected 6 h after omentum-derived ASC transplantation into APAP-treated mice and used for RT-PCR (a, b, c and d) and western blot (e) analysis. (f) CYP 450 2E1, CYP 450 1A2, NTR, and 4-HNE protein expression by western blot analysis. (g) CYP2A5 gene expression by RT-PCR. The data are expressed as the means ± SEM, n ≥ 5, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
