Fig. 1.
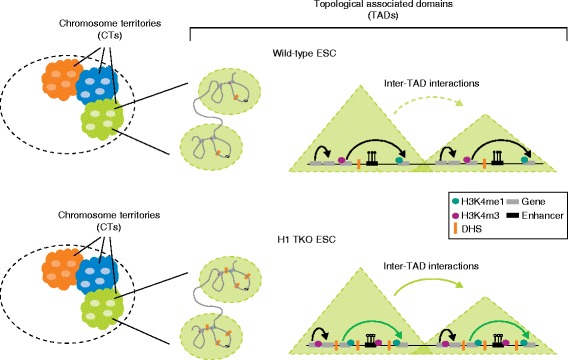
The effects of depletion of histone H1 on genome architecture. (Top panels) In interphase, chromosomes are organized in distinct chromatin territories (CTs) that are cytologically defined. Within a CT, the chromosome is structurally organized into distinct topological-associated domains (TADs). Within individual TADs, regulatory elements, such as enhancers and gene promoters, can be engaged in looping interactions. (Bottom panels) In H1 triple–knockout (TKO) embryonic stem cells (ECSs), the overall genome organization into TADs is not majorly affected. However, within gene-dense TADs, long-range inter-TAD interactions increase and new DNAse hypersensitive sites (DHSs) and sites of histone H3 lysine 4 mono-methylation and trimethylation (H3K4me1 and H3K4me3, respectively) are established
