Fig. 1.
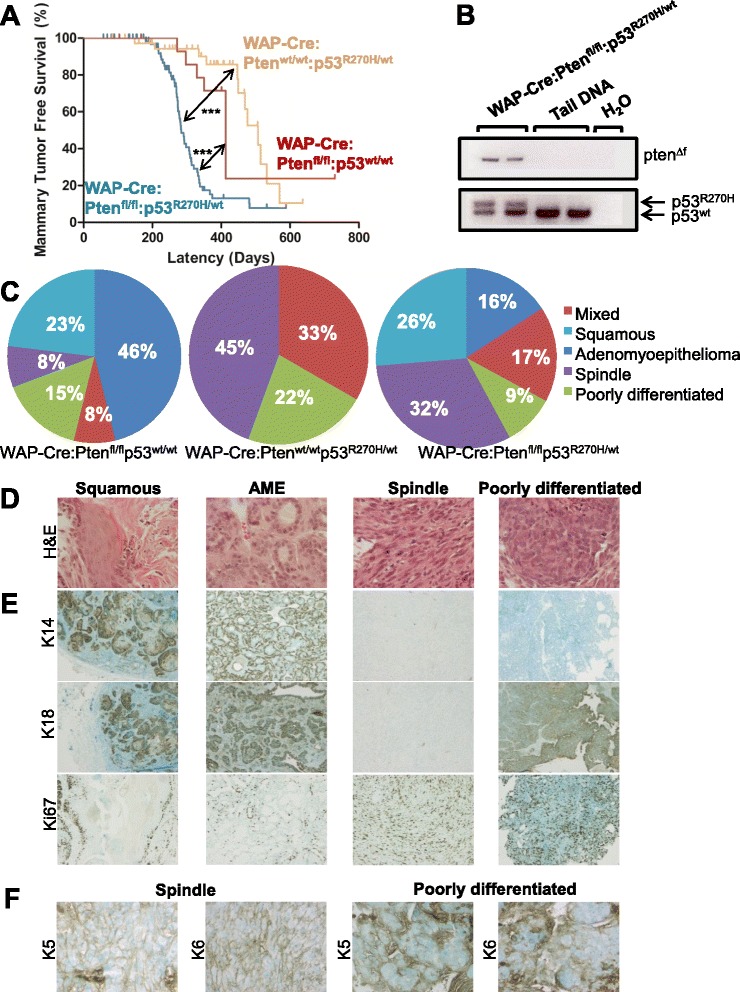
Pten deletion plus p53-R270H point mutation cooperate to accelerate mammary tumor formation. a Kaplan-Meier mammary tumor-free curves for WAP-Cre:Ptenfl/fl:p53wt/wt (n = 16; median latency - 413 days), WAP-Cre:Ptenwt/wt:p53R270H/wt (n = 39; median latency - 507 days), and WAP-Cre:Ptenfl/fl:p53R270H/wt (n = 75; median latency - 291 days) mice. Statistical significance by Wilcoxon method: Pten versus p53, p = 0.0118; Pten/p53 vs. Pten, p < 0.0001; Pten/p53 vs. p53, p < 0.0001. b Detection of conditional Pten deletion and p53 mutant allele by PCR. c Distribution of tumor types (%) in WAP-Cre:Ptenfl/fl:p53wt/wt (left; n = 13), WAP-Cre:Ptenwt/wt:p53R270H/wt (middle; n = 9), and WAP-Cre:Ptenfl/fl:p53R270H/wt (right; n = 76) mice. d Histology of the four major tumor types from WAP-Cre:Ptenfl/fl:p53R270H/wt mice. Original magnification 40×. Larger images are presented in Additional file 1. e Representative IHC analysis of basal differentiation marker (K14), luminal differentiation marker (K18) and proliferation marker ki67 in the major tumor types from WAP-Cre:Ptenfl/fl:p53R270H/wt mice. f Representative expression of basal differentiation marker (K5 and K6) in PDA (n = 7) and spindle (n = 3) tumors. IHC immmunohistochemistry, PCR polymerase chain reaction, PDA poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma
