Abstract
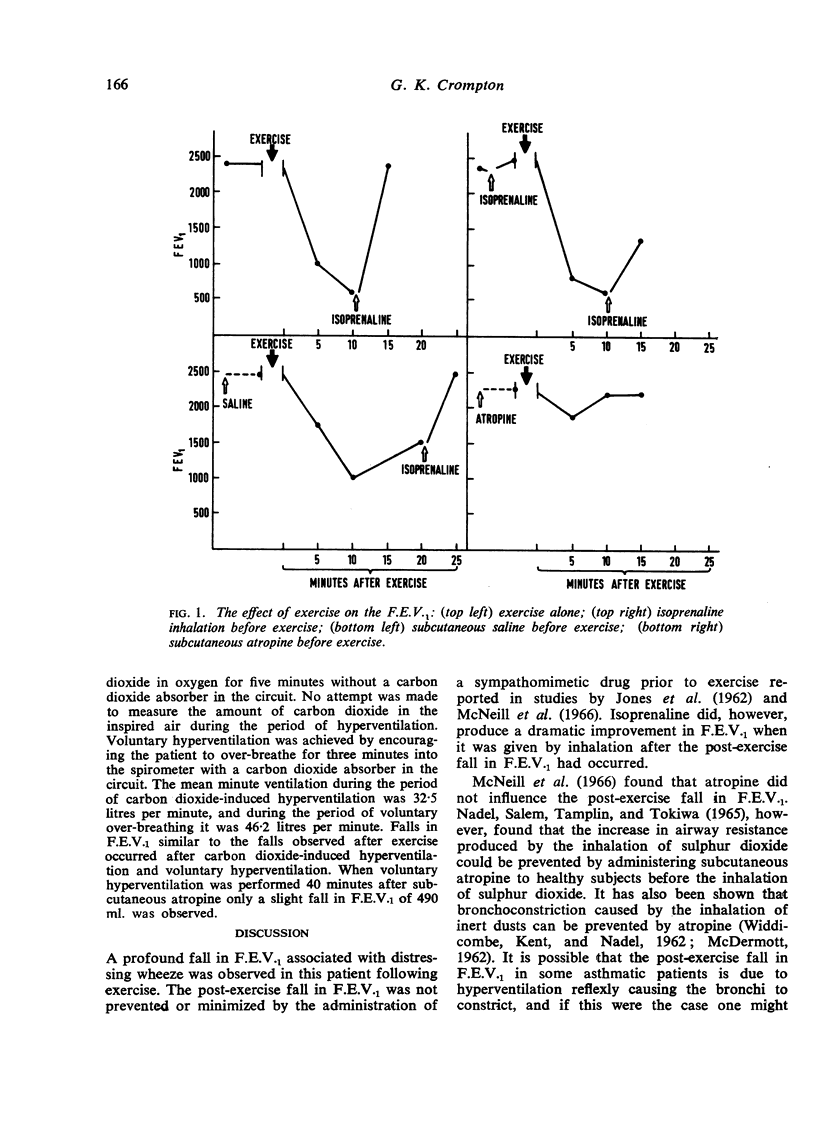
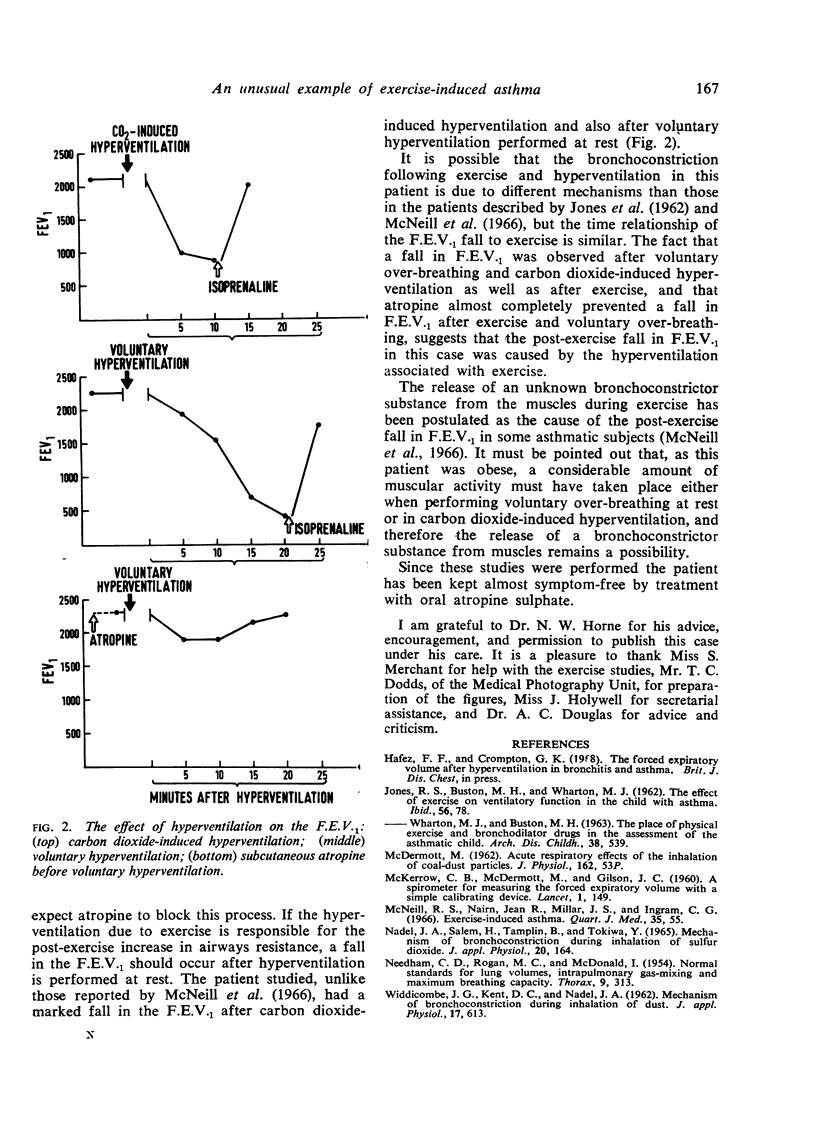
A patient with exercise-induced asthma is described in whom the post-exercise fall in F.E.V.1 was not prevented by the inhalation of isoprenaline immediately before exercise but was almost completely prevented by subcutaneous atropine given 40 minutes before exercise. A large fall in F.E.V.1 similar to the fall after exercise occurred after carbon dioxide-induced hyperventilation and voluntary hyperventilation performed at rest. Only a slight fall in F.E.V.1 occurred when atropine was given before voluntary hyperventilation was performed. It is postulated that the post-exercise fall in F.E.V.1 in this patient is due to hyperventilation reflexly causing bronchial constriction.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- JONES R. S., BUSTON M. H., WHARTON M. J. The effect of exercise on ventilatory function in the child with asthma. Br J Dis Chest. 1962 Apr;56:78–86. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(62)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES R. S., WHARTON M. J., BUSTON M. H. THE PLACE OF PHYSICAL EXERCISE AND BRONCHODILATOR DRUGS IN THE ASSESSMENT OF THE ASTHMATIC CHILD. Arch Dis Child. 1963 Dec;38:539–545. doi: 10.1136/adc.38.202.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NADEL J. A., SALEM H., TAMPLIN B., TOKIWA Y. MECHANISM OF BRONCHOCONSTRICTION DURING INHALATION OF SULFUR DIOXIDE. J Appl Physiol. 1965 Jan;20:164–167. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1965.20.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM C. D., ROGAN M. C., McDONALD I. Normal standards for lung volumes, intrapulmonary gas-mixing, and maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):313–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDICOMBE J. G., KENT D. C., NADEL J. A. Mechanism of bronchoconstriction during inhalation of dust. J Appl Physiol. 1962 Jul;17:613–616. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1962.17.4.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


