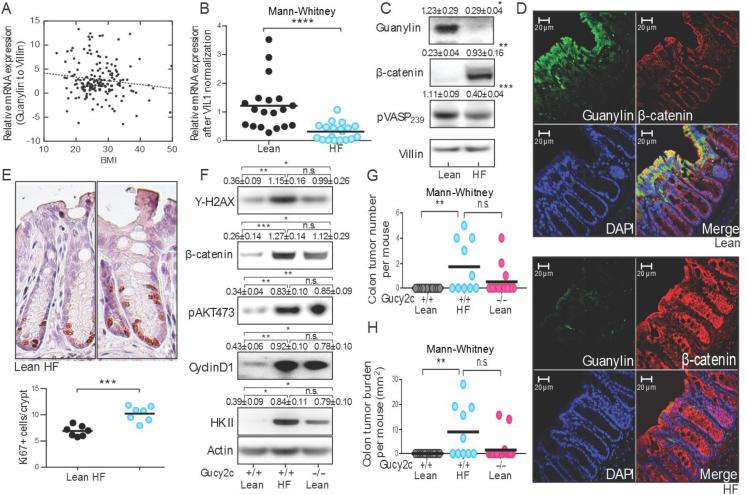
Figure 1. Suppression of the guanylin-GUCY2C axis with epithelial dysfunction and tumorigenesis in obesity in C57BL/6 mice.
(A) Guanylin mRNA in human colon inversely correlates with BMI. (B) Guanylin mRNA in colons from mice on high fat (HF) or Lean diets. (C) Loss of guanylin in mice on HF diet silences GUCY2C, increasing epithelial dysfunction. (D) Guanylin (green), β-catenin (red) and (E) Ki67 in colons from mice on Lean and HF diets. (F) Epithelial dysfunction was compared in GUCY2C wild type (+/+) and deficient (−/−) mice on Lean and HF diets. (G) Tumor number and (H) burden in GUCY2C (+/+) and (−/−) mice on Lean or HF diet receiving AOM. Immunoblot results represent the mean ± SEM of 5 mice.