Figure 3.
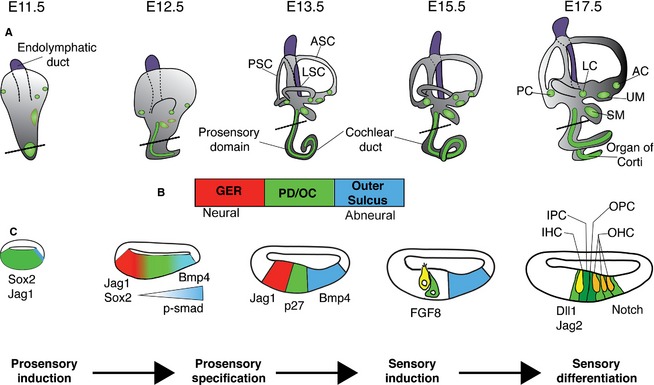
Development and specification of the prosensory domain (PD) and the organ of Corti (OC). (A) Time course of inner ear development, viewed from the lateral side of the embryo. Between E11.5 and E17.5, the cochlear duct elongates from the ventral wall of the otocyst. Between E12.5 and E13.5, the plates in the vestibular portion undergo extensive rearrangement to form the semicircular canals with cristae (green circles) developing at their base. By E15.5, the vestibular labyrinth and its associated sensory organs have developed (cristae and maculae are shown in green, the approximate position of maculae at E11.5 and E12.5 are shown with red outlines), while the OC continues to differentiate. (B) The bar represents the orientation of the cochlear sections shown in (C). The PD, which gives rise to the OC, is flanked by non‐sensory tissue. On the neural side the PD is flanked by the greater epithelial ridge (GER; red) and on the abneural side by the cells that will form the outer sulcus (blue). (C) Schematic diagrams of cochlear sections at the level of the dotted lines shown in (A). Initially the sensory competent region of the cochlea expresses Sox2 and Jag1. A gradient of BMP4 (visualized by the readout of phosphorylated SMAD1/5/8) from the abneural side of the cochlea refines the prosensory region as development proceeds. By E13.5, cells in the PD exit the cell cycle and contain all the progenitors for the OC. At E14.5, at the border between the GER and the PD, inner hair cells (IHCs) in the base of the cochlea begin to differentiate in response to an as‐yet unidentified signal. As IHCs differentiate, they become a source of FGF8, which together with Notch signaling will help establish the patterning of the OC. By E17.5, the base of the cochlea exhibits its final pattern of one row of IHCs and three rows of outer hair cells (OHCs). Over the next 2 days, this patterning will extend throughout the length of the cochlea. The endolymphatic duct, which grows out from the medial side of the otocyst, is colored purple to distinguish it from the rest of the inner ear. AC, anterior crista ampullaris; ASC, anterior semicircular canal; IPC, inner pillar cell; LC, lateral crista ampullaris; LSC, lateral semicircular canal; OPC, outer pillar cell; PC, posterior crista ampullaris; PSC, posterior semicircular canal; SM, saccular macula; UM, utricular macula.
