Figure 1.
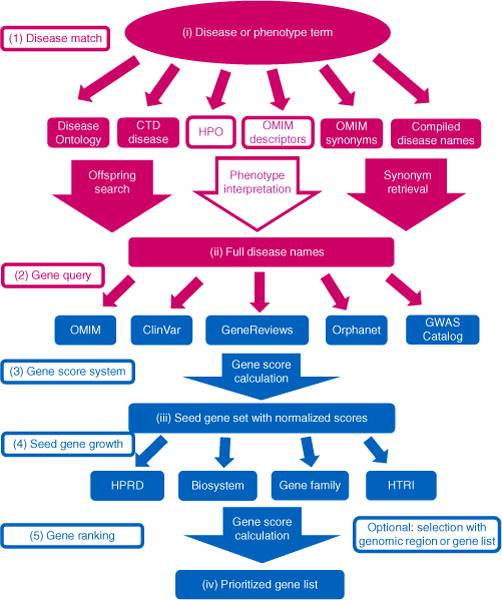
Workflow of Phenolyzer. (1) Disease match: each disease or phenotype query term is separately translated into sets of disease names by word match, offspring search, synonym retrieval and phenotype interpretation in disease name databases. (2) Gene query: each retrieved disease name is queried in the gene-disease databases based on an exact match, to get a list of genes. (3) Gene score system: a score based on the type and confidence of the gene-disease relationship is generated for each gene corresponding to each disease name. Then, for each input term, a weighted sum score is calculated for each reported gene by adding all the scores retrieved in previous step. The seed gene set is generated by collating all the genes of all input terms, and each gene score is normalized. (4) Seed gene growth: candidate disease genes are expanded beyond the seed gene set based on four types of gene-gene relationships; scores are calculated for all genes that connect with seed genes. (5) Gene ranking: all the information is integrated to generate a score for each gene, with the weights trained from a logistic regression model. The scores are renormalized to the final prioritized gene list. HPRD, Human Protein Reference Database; HTRI, Human Transcriptional Regulation Interaction Database.
