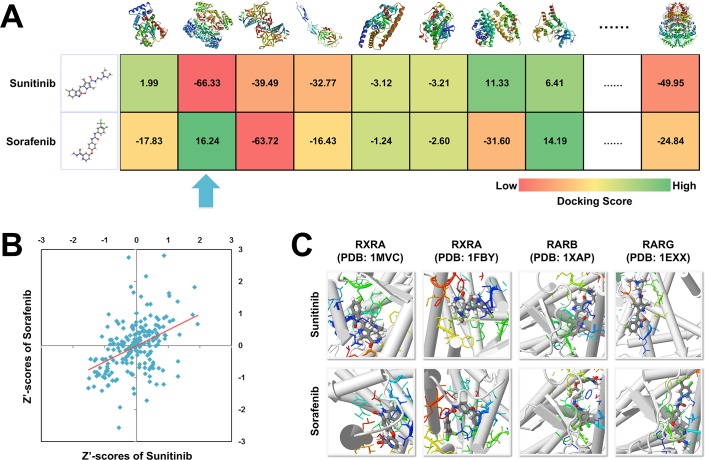
Fig 1. Structural comparison of sunitinib and sorafenib towards potential off-targets.
(A) The rationale of the comparison between sunitinib and sorafenib. Simulated binding affinity is measured by docking scores. We pay particular attention to those targets (as indicated by the arrow) showing much higher affinity with sunitinib than with sorafenib. (B) The comparability between sunitinib and sorafenib is verified by their positively correlated Z’-score vectors. (C) The whole molecule of sunitinib binds deep into the pockets of retinoic acid receptors (RXRA has two structure models in Protein Data Bank for docking, while RARB and RARG have one). In contrast, the sorafenib molecule is less well accommodated in the pockets due to steric hindrance in different directions. As suggested by docking scores, the binding strengths of sunitinib towards retinoic acid receptors tend to be higher than those of sorafenib. The figures are produced by DRAR-CPI server.