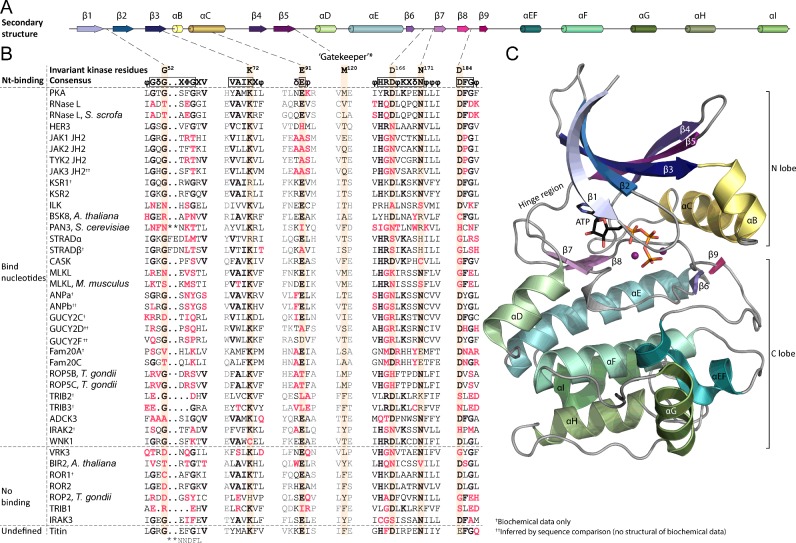
Figure 1. Conserved motifs and residues contributing to nt binding and kinase activity in (pseudo)kinases.
(A) Schematic depiction of the secondary structure elements of ePKs. Relative sizes and positions of elements are based on PKA (PDB: 4WB5). (B) Sequence alignment of selected pseudokinases and PKL proteins classified based on current information on nt binding. Conserved PK regions relevant to nt binding are shown. The six highly conserved residues contributing directly to nt binding or catalytic activity are highlighted. *The gatekeeper residue is not part of the 10 conserved kinase residues identified in [14]. All sequences represent human proteins unless otherwise noted. The sequence alignment was made using Clustal W [137,138] and manually corrected based on crystal structures and previous alignments [32,92,139] where available. For non-ePKs the sequences shown are the (predicted) functional/structural equivalents of the conserved residue in question (secondary structure of e.g. ADCK3 or Fam20 kinases is different from the one shown in A). Fam20C is included as an example of an active Fam20 kinase. (C) 3D structure of human PKA (PDB: 4WB5) shown as an example of an archetypal ePK. ATP is shown in sticks and the two magnesium cations as purple spheres. Colours of secondary structure elements are as in (A).