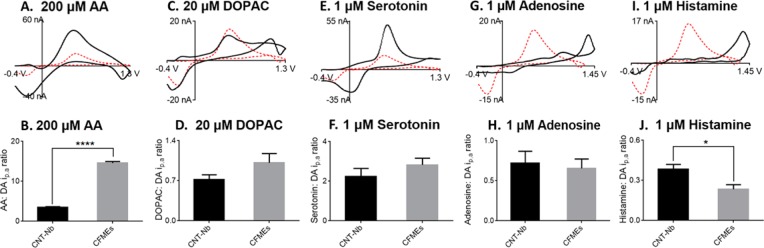
Figure 5.
Detection of other neurochemicals at CNT-Nb microelectrodes. (Upper row) CVs of (A) 200 μM AA, (C) 20 μM DOPAC, (E) 1 μM serotonin, (G) 1 μM adenosine, and (I) 1 μM histamine in PBS buffer. Red dashed line is CV of 1 μM dopamine obtained from the same CNT-Nb electrode. For AA, DOPAC, and serotonin, the electrode was scanned to 1.3 V; for adenosine and histamine, the electrode was scanned to 1.45 V. (Lower row) Column plots show the ratio of oxidation current for (B) 200 μM AA, (D) 20 μM DOPAC, (F) 1 μM serotonin, (H) 1 μM adenosine, and (J) 1 μM histamine compared to the corresponding oxidation current of dopamine at CNT-Nb microelectrode (black, n = 5) and CFMEs (gray, n = 5). The oxidation current ratios at CNT-Nb microelectrodes are significantly different than CFMEs for the measurement of ascorbic acid (paired t test, p < 0.0001) and histamine (paired t test, p < 0.05).