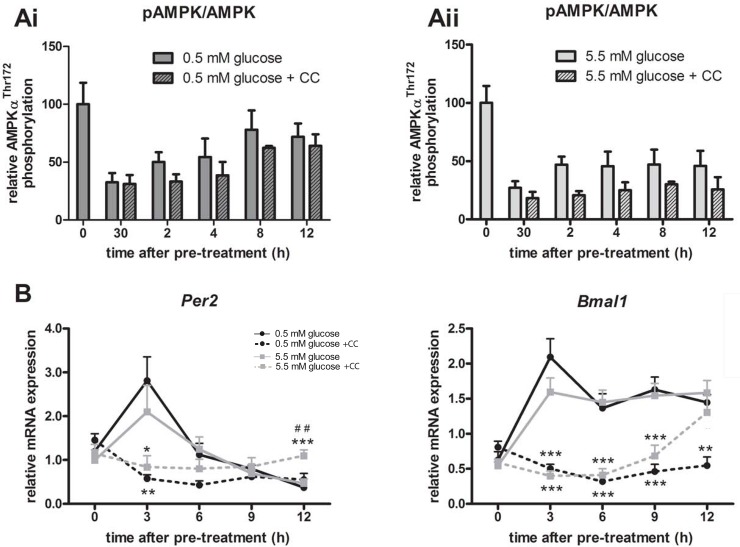
Fig 4. Effects of Compound C on phosphorylation status of AMPK and the transcriptional expression profile of Per2 and Bmal1.
After serum starvation, cells were pre-treated with 25 μM Compound C (CC), followed by replacement of the media with either 0.5 or 5.5 mM glucose in the absence or presence of 12.5 μM CC. This was considered time 0. Protein and RNA was harvested at indicated time points. Ai) Relative levels of AMPK phosphorylation in mHypoE-37 neuronal cells in 0.5 mM and Aii) 5.5 mM glucose-containing media in the absence or presence of 12.5 μM of the AMPK inhibitor Compound C (CC). Shown is the densitometric analysis of the ratio of phosphorylated over total protein. B) Treatment with 12.5 μM Compound C significantly alters Per2 and Bmal1 transcriptional expression profile in mHypoE-37 neuronal cells. Cells were harvested every three hours during 12 hours and transcriptional expression was measured using qRT-PCR. Compound C inhibited Per2 expression at 3 hours after media replacement, and increased Per2 expression at 12 h after media replacement. The transcriptional expression of Bmal1 was suppressed by CC at every time point *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001 between glucose with and without CC. ##: p<0.01 between 0.5 mM glucose + CC and 5.5 mM glucose + CC. Determined by repeated measures ANOVA, followed by one-way ANOVA for each individual time point with a Tukey’s post-hoc test. All values are relative to mRNA levels of Histone 3a. Mean ± SEM of 4 independent experiments.