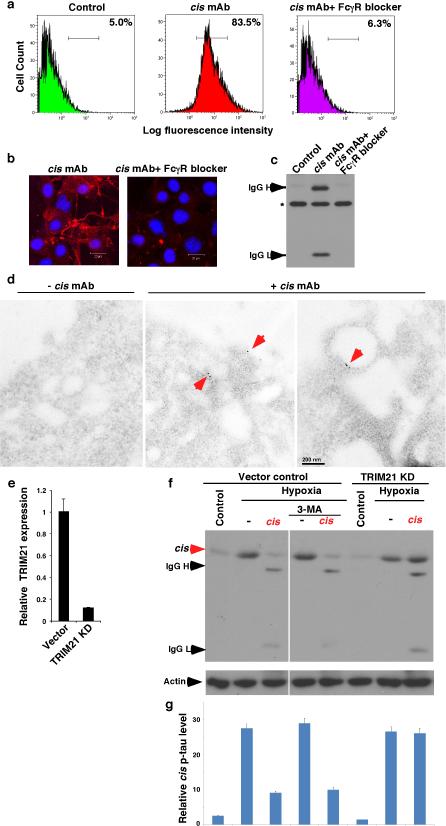
Extended Data Figure 7. Inhibition of FcγR binding blocks cis mAb from entering neurons and TRIM21 KD fully prevented cis antibody from ablating cis p-tau in neurons.
a-d, Inhibition of FcγR binding potently blocks cis mAb from entering neurons. cis mAb was added to neurons in the absence or presence of a human FcγR-binding inhibitor, followed by detecting the binding of cis mAb to the cell surface by FACS (a), entry of cis mAb into cells by IF (b), IB (c) and electron microscopy after immunogold labeling (d). The FcR binding inhibitor fully blocked cis mAb from binding to the cell surface and entering neurons. Electron microscopy showed that cis mAb bounds to the cell surface and endocytic vesicles (red arrows). e, f, TRIM21 knockdown fully prevented cis antibody from ablating cis p-tau in neurons. TRIM21 was stably knocked down in SY5Y neuronal cells using a validated TRIM21 shRNA lentiviral vector and confirmed by real-time RT-PCR analysis of TRIM21 mRNA expression (e). TRIM21 knockdown or vector control SY5Y cells were subjected to hypoxia treatment in the presence or absence of cis mAb and/or 3-Methyladenine, an autophagy inhibitor, followed by IB, followed by quantifying cis p-tau levels normalized actin levels (lower panel) (f).