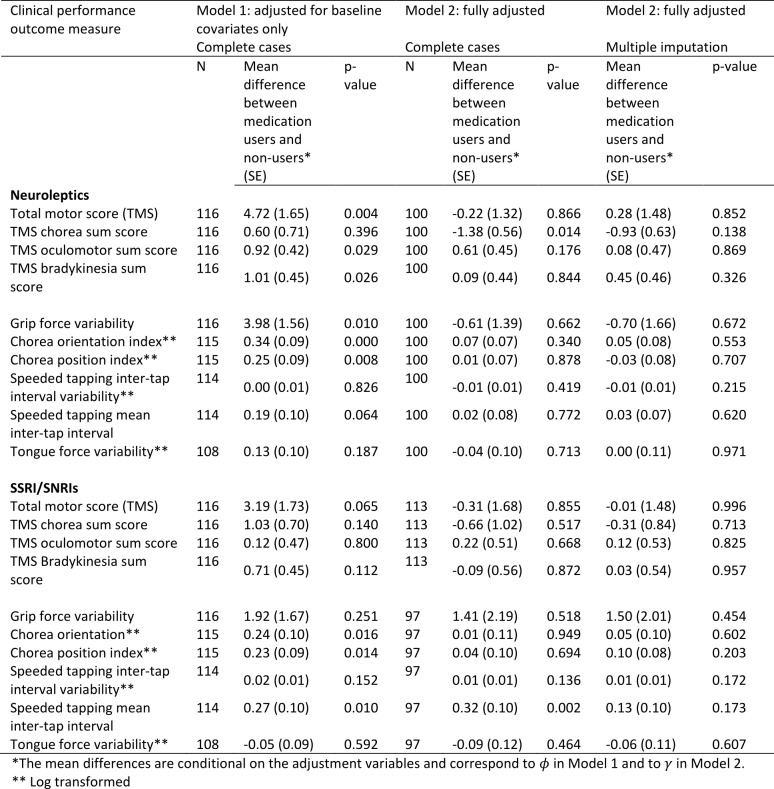
Table 4: Associations between medication use and performance on motor tasks and Q-Motor tasks using Model 1 (adjusted for baseline covariates only – sex, disease group, age, CAG, study site, education) and Model 2 (fully adjusted - for baseline covariates, prior medication use, use of other medications, prior performance measures). The models were first fitted on complete cases with no dropout or other missing data (N). Model 2 was then fitted by using multiple imputation to impute missing data.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.