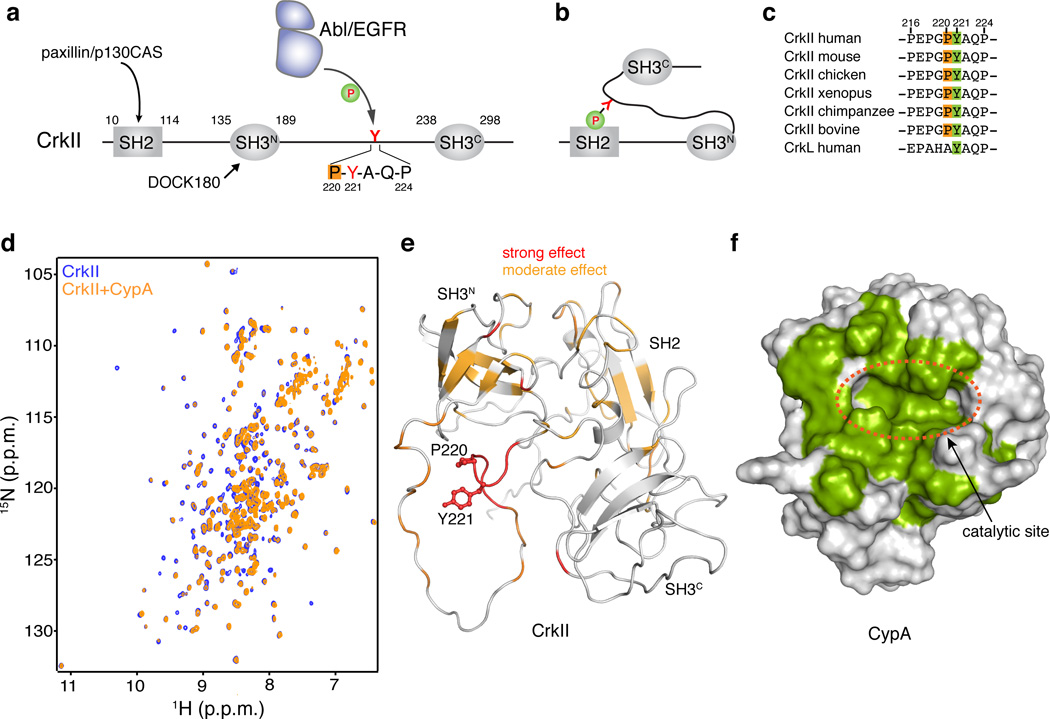
Figure 1. Binding between CypA and CrkII.
(a) Domain organization of human CrkII. Tyr221 and the Pro220 residues are highlighted. (b) Phosphorylation of Tyr2211 in CrkII results in intramolecular interaction between pTyr221 and the SH2 domain of CrkII. (c) Sequence alignment of the region Pro216-Pro231 of CrkII from different species. (d) Overlaid 1H-15N HSQC NMR spectra of labeled CrkII (blue) and equimolar unlabeled CypA (orange). (e) Chemical shift mapping of the effect of CypA binding to CrkII. A stretch of ~6 residues flanking Pro220 and encompassing Tyr221 is most affected. CrkII is shown in a ribbon representation (PDB ID 2EYZ). Tyr221 and Pro220 side chains are shown as sticks. (f) Chemical shift mapping of the effect of CrkII binding to CypA. CypA residues strongly affected by CrkII binding are colored green. CypA is shown as a solvent-accessible surface