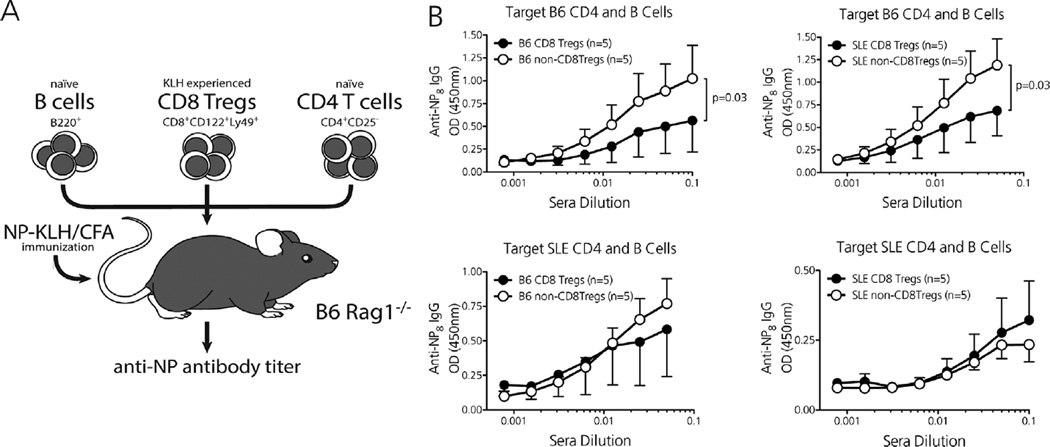
Figure 3. Effector CD4 T and B cells from lupus-prone mice resist CD8Treg-mediated suppression.
(A) In vivo CD8Treg suppression assay in which KLH-activated CD8Tregs and naïve CD4+ CD25−T cells/whole B220+ B cells are transferred to immunodeficient B6.RAG recipients that are immunized and boosted with the test stimulus NP-KLH. A similar crossover platform was used as described in Figure 2A. (B) CD8Tregs from B6 and B6.SLE123 mice potently suppress the high-affinity anti-NP8 IgG response when targeting nonautoimmune CD4/B cells (top). Effector CD4/B cells from lupus-prone B6.SLE123 mice resist suppression when targeted byCD8Tregs from either B6 or B6. SLE123 mice (bottom). N = 5 mice per experimental group. Significance determined by performing a semilogarithmic linear regressional analysis followed by y-intercept and slope curve comparison.