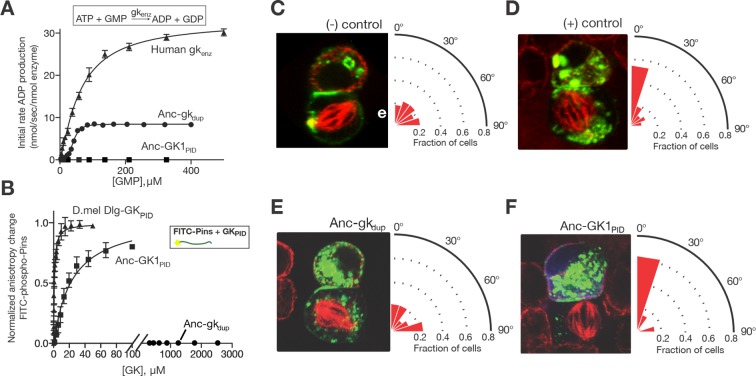
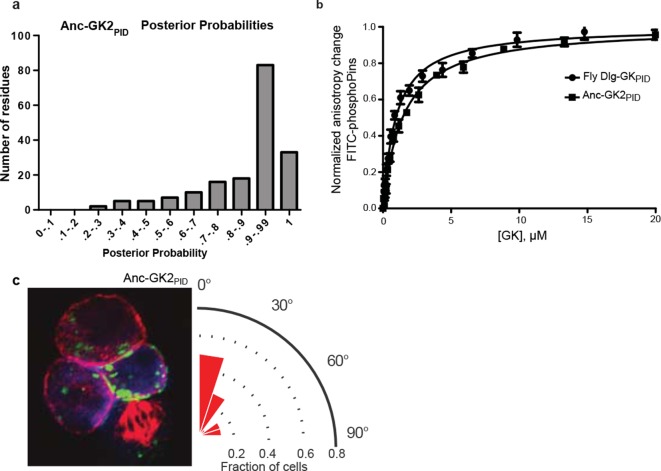
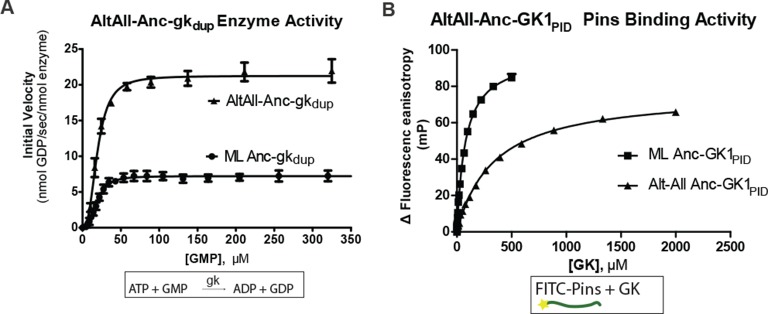
Figure 2. Evolution of a novel spindle-orientation function in ancestral GKPID.
(A) Anc-gkdup (circles) is an active nucleotide kinase in a coupled enzyme assay for the reaction shown; Anc-GK1PID (boxes) is inactive. Activity of the human gk enzyme (triangles) is shown for reference. Error bars show SEM for three replicates. (B) The more recent ancestral protein Anc-GK1PID (boxes) binds a 20 amino-acid peptide (see methods) from the Pins protein in a fluorescent anisotropy assay, but Anc-gkdup (cirlcles) does not. Pins binding by the GKPID of the Drosophila melanogaster Dlg protein (triangles) is shown for reference. Error bars show SEM for three replicates. (C–F) Evolution of spindle orientation function as assayed in cultured S2 cells that do not express endogenous Dlg protein. Cells were transfected with a GK construct (C, –control: empty transfection vector; D, + control: GKPID from extant Drosophila Dlg) and scored for alignment of the mitotic spindle (red, tubulin, visualized immunocytochemically) relative to the Pins cortical crescent (green, a GFP-tagged Pins-Ecd fusion). In the example images for each experiment, two cells are shown, the bottom one of which is dividing. The angle of the mitotic spindle relative to a line bisecting the Pins crescent (from 0°, precisely aligned, to 90°) was recorded in many dividing cells; the radial histogram (right) shows the distribution of observed angles among all cells scored with a given genotype. Cells transfected with Anc-gkdup (E) do not display robust spindle orientation, but those transfected with Anc-GK1PID do (F). SEM: Standard error of the mean.