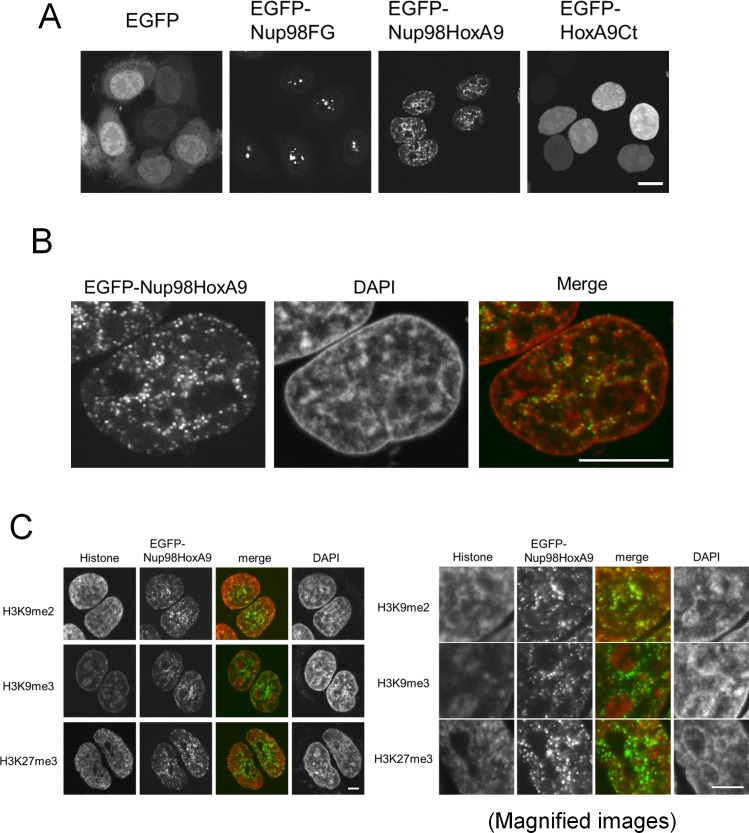
Figure 1. Nup98-HoxA9 dots associate with facultative heterochromatin.
(A) Subcellular localization of Nup98-HoxA9 and its truncated mutants. EGFP, EGFP-Nup98FG, EGFP-Nup98-HoxA9, or EGFP-HoxA9-Ct expressing plasmids were transfected into HeLa cells for 24 hr and observed. Bar, 10 μm. (B) Confocal microscopy analysis of EGFP-Nup98-HoxA9 in HeLa cells. A merged image shows EGFP-Nup98-HoxA9 (green) and DAPI (red). Bar, 10 μm. (C) Association of Nup98-HoxA9 dots with specific histone modifications. HeLa cells were transfected with the EGFP-Nup98-HoxA9 expressing plasmid. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were fixed and stained with antibodies against indicated histone modifications. DAPI staining was used to visualize the nuclei. Bar, 5 μm. DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein.
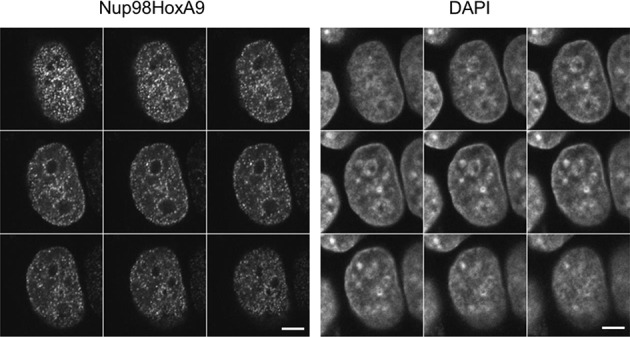
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Serial z-sectioning of EGFP-Nup98-HoxA9 in HeLa cell.