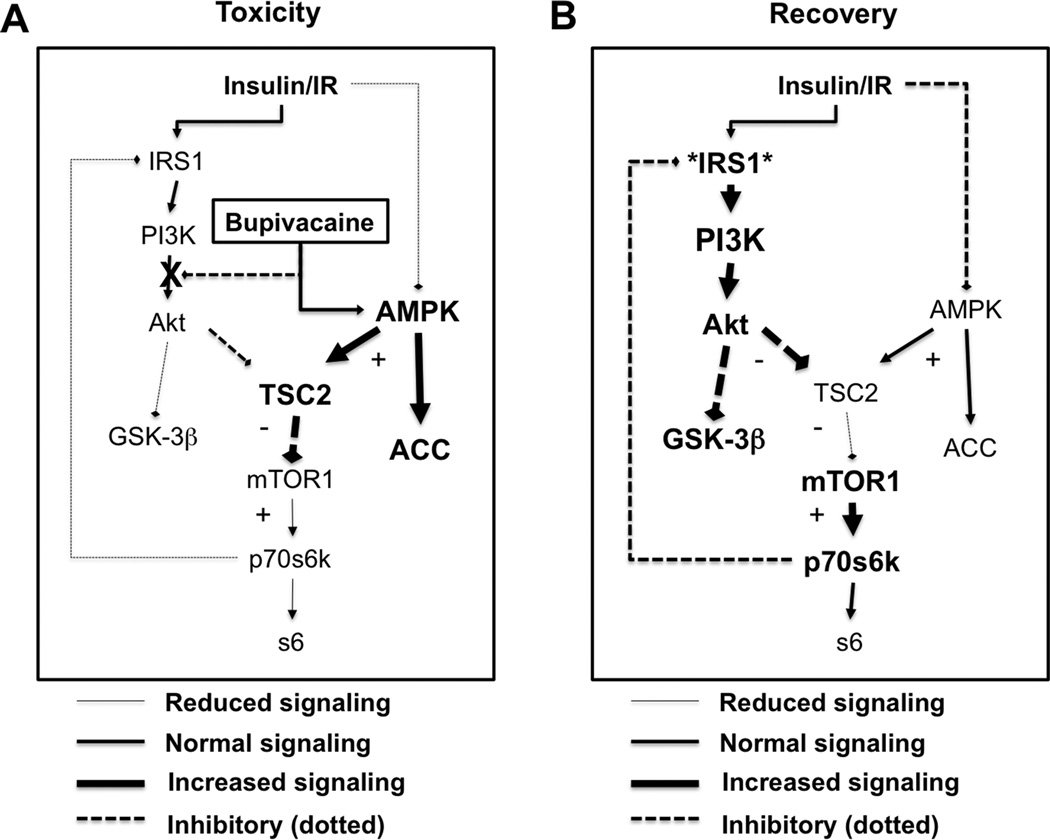
Figure 10. Schematic of induction of and recovery from bupivacaine toxicity.
A. During toxicity, bupivacaine activates 5’ adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK) with phosphorylation of threonine 172 and blocks protein kinase B (Akt) with reduction of phosphorylation at serine 473 and some reduced phosphorylation of Threonine 308. These two effects converse at tuberous sclerosis 2 (TSC2). AMPK activates TSC2 by phosphorylating it at serine 1387 with a decrease of inhibition of TSC2 by Akt. Kinases downstream of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTOR1) including p70 s6 kinase (p70s6k) and ribosomal protein s6 (s6) will be less activated. Feedback inhibition of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) by p70s6k is lost leading to sensitization of insulinergic signaling. B. During recovery, IRS1 is hyper-sensitized so at equivalent insulinergic stimulation there will be a hyper-activation of kinases downstream of IRS1 including Akt and glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β). Both of these proteins can control and assist with recovery of cardiac contractility. AMPK remains phosphorylated and targets downstream of TSC2 and mTOR1 remain un-activated.