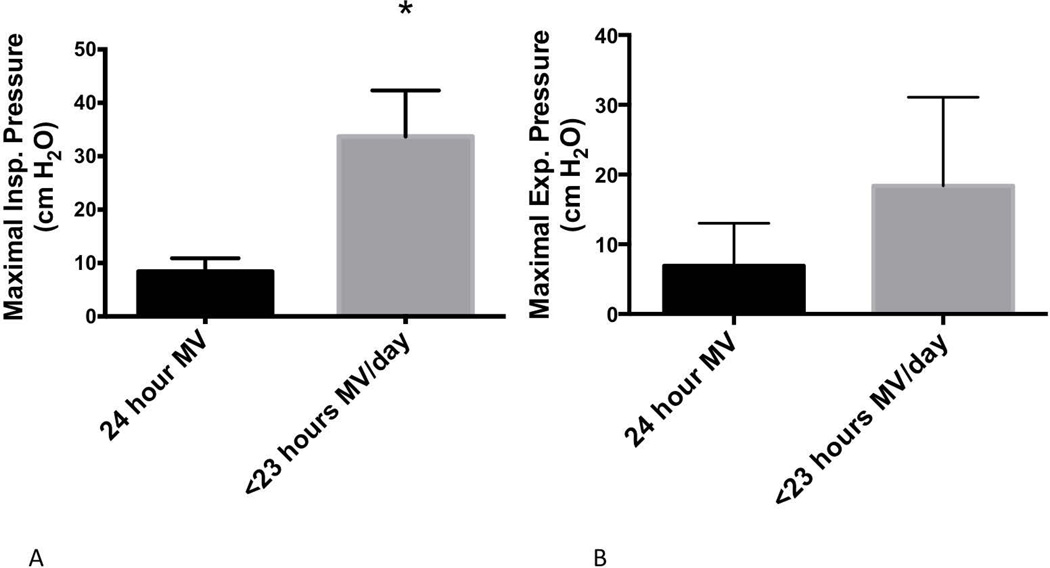
Figure 2.
Maximal respiratory pressures in ventilator-dependent participants with CNM. Participants were grouped according to their routine practice of independent breathing. (A) Maximal inspiratory pressure was significantly higher in participants who routinely breathed without MV for at least 1 hour daily (P<0.05). (B) Maximal expiratory pressure also trended higher among participants with more routine independent breathing, but this difference was not statistically significant (P = 0.10).