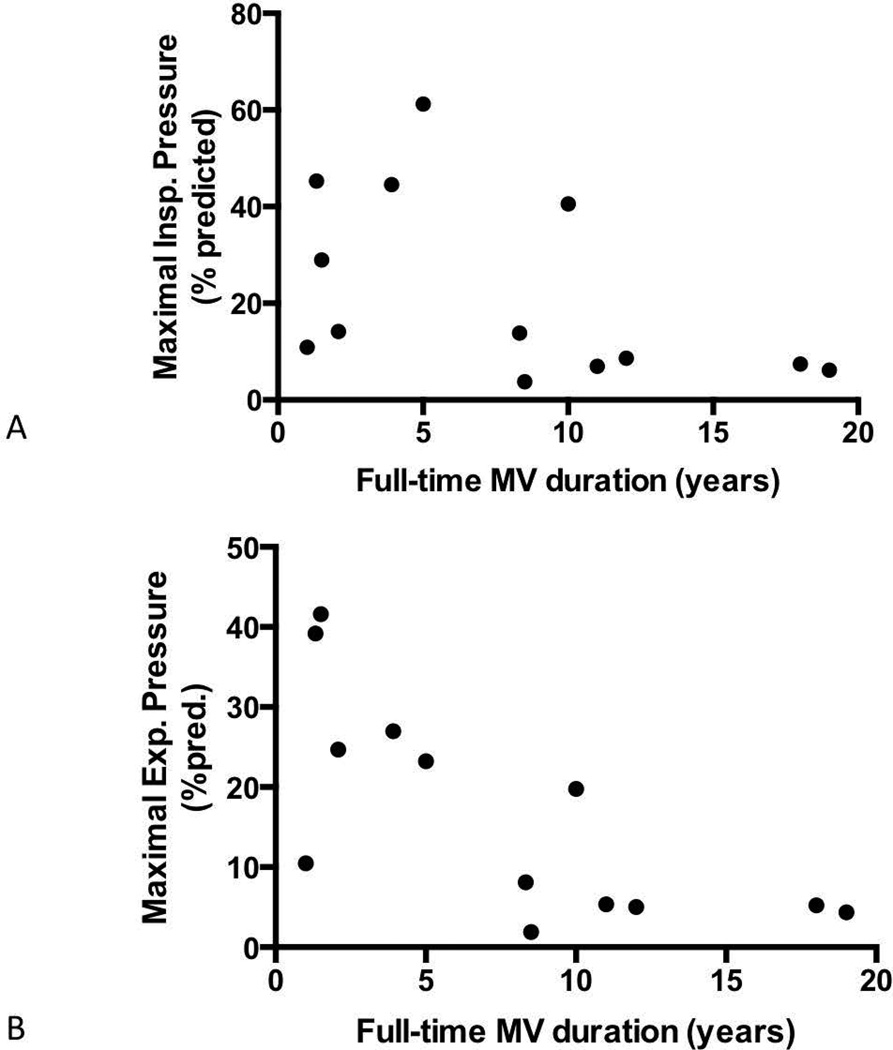
Figure 3.
Relationship between duration of invasive MV dependence and maximal respiratory pressures. (A) While predicted maximal inspiratory pressure was generally lower after prolonged periods of mechanical ventilation, it was not associated significantly with the duration of ventilator dependence (r = −0.482, P = 0.10). (B) In contrast, duration was significantly associated with predicted maximal expiratory pressure (r = −0.715, P<0.01).