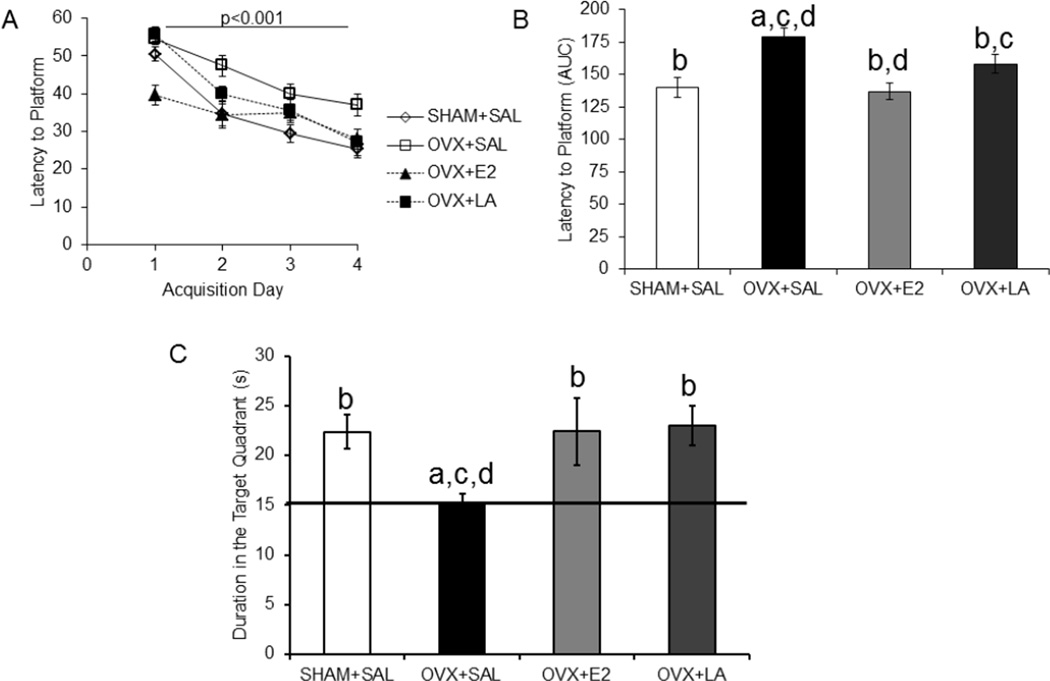
Figure 2. Leuprolide acetate rescues deficits on the Morris water maze task with no delay of treatment after OVX.
In the no delay cohort, where treatment began on the day of OVX, OVX-associated cognitive dysfunction in the Morris water maze was rescued by 8 weeks of treatment with leuprolide acetate or E2. A: Animals were successfully trained over a four day period. B: Bar graphs represent area under the curve (AUC) for accumulative latency to the platform during training. Leuprolide acetate and E2 had a lower latency to the platform (repeated measure ANOVA). C: The duration the animal spent in the target quadrant was used to analyze the sixty second probe trial, where the platform was removed. E2 and leuprolide acetate treated animals spent a higher percentage of time in the target quadrant as compared to the ovariectomized group (one-way ANOVA). Results are expressed as mean ± sem. Significant difference (p<0.05) from SHAM+SAL (a), from OVX+SAL (b), from OVX+LA (c) and from OVX+E2 (d)
SHAM+SAL, sham ovariectomy treated with saline; OVX+SAL, ovariectomy treated with saline; OVX+E2, ovariectomy treated with 17β-estradiol; OVX+LA, ovariectomy treated with leuprolide acetate