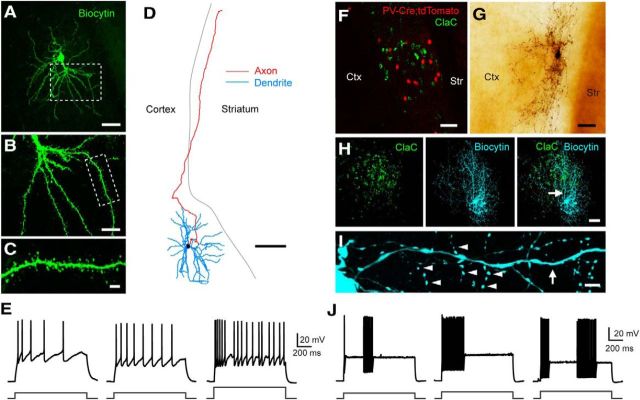
Figure 2.
Morphological and electrophysiological properties of retrogradely labeled ClaC neurons and PV claustral neurons. A, Low-magnification image of a retrogradely labeled ClaC neuron filled with biocytin (green). B, Higher-magnification view of the robust proximal dendrites and further dendritic branching of this cell in the region outlined by the white box in A. C, Higher-magnification view of the dendrite and dendritic spines of the region outlined by the white box in B. D, Morphological reconstruction of a second biocytin-filled ClaC neuron. Dendrites are shown in blue, axons in red. Note the long axonal branch coursing through the white matter toward the cortex. E, Current-clamp recordings of the responses of three different ClaC neurons during injections of a 1 s depolarizing current pulse (left and middle, 100 pA; right, 200 pA). F, Image of retrogradely labeled ClaC neurons (green) and PV neurons (red) in a coronal section from a PV-Cre;tdTomato mouse. G, Image of a PV neuron filled with biocytin. H, Image of retrogradely labeled ClaC neurons (left, green) and a second biocytin-filled PV neuron (middle, blue). The superimposed images show the correspondence between the PV neuron's axonal and dendritic processes and the region containing retrogradely labeled ClaC cells in the claustrum (right). The arrow indicates the location of the dendrite shown at higher magnification in I. I, A higher-magnification view of the PV neuron in H showing a smooth dendrite (arrow) and examples of the neuron's many axonal boutons (arrowheads). J, Current-clamp recordings of responses from three different claustral PV neurons during injections of 1 s depolarizing current pulses (left, 300 pA; middle, 370 pA; right, 400 pA). Ctx, Cortex; Str, striatum. Scale bars: A, 50 μm; B, 20 μm; C, 5 μm; D, 100 μm; F–H, 50 μm; I, 5 μm.