Figure 3.
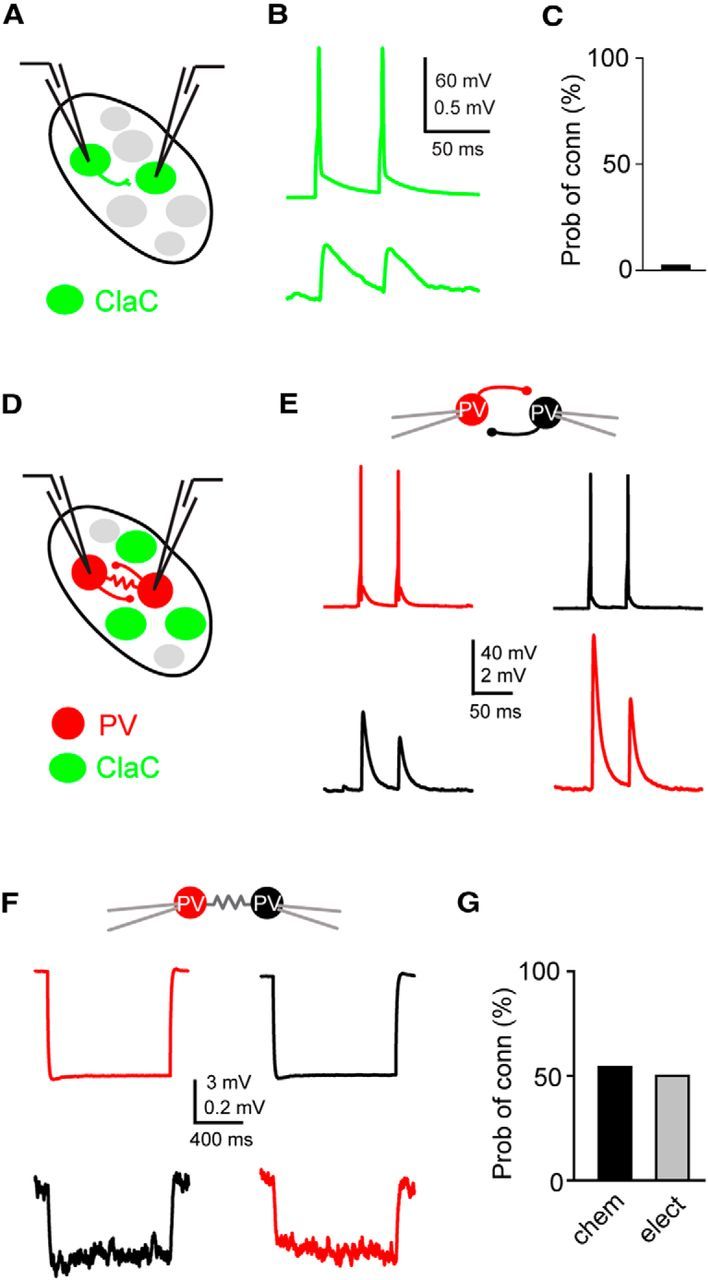
ClaC neurons are sparsely interconnected within the claustrum, whereas PV claustral neurons form frequent chemical and electrical synaptic connections. A, Schematic of a paired recording from two retrogradely labeled ClaC neurons. B, Average synaptic response recorded in a ClaC neuron (bottom trace) following action potentials induced in a presynaptic ClaC cell (top trace) during simultaneous recordings from a pair of monosynaptically connected ClaC neurons. C, The frequency of identified connections among ClaC connections tested (2 connections identified in 86 connections tested). D, Schematic of a paired recording from two claustral PV neurons. E, Bidirectional chemical synaptic connections between two simultaneously recorded PV neurons in the claustrum. Action potentials in each presynaptic PV neuron (top traces) evoked synaptic responses in the simultaneously recorded postsynaptic PV neuron (bottom traces). The postsynaptic potentials are depolarizing because the recordings were performed with a high-chloride internal solution. This pair of PV neurons was not electrically coupled. F, Electrical synaptic connections between two PV claustral neurons. A hyperpolarizing current step (−100 pA, top traces) evoked a corresponding response in the electrically connected partner (bottom traces) during simultaneous recordings from an electrically connected pair of PV neurons. G, Summary data showing the probability of connection for chemical (n = 13 of 24 tested connections) and electrical synaptic connections (n = 6 of 12 tested connections). The configurations for the identified connections were as follows: PV→PV: one pair; PV↔PV: two pairs; PV PV: zero pairs; PV
PV: zero pairs; PV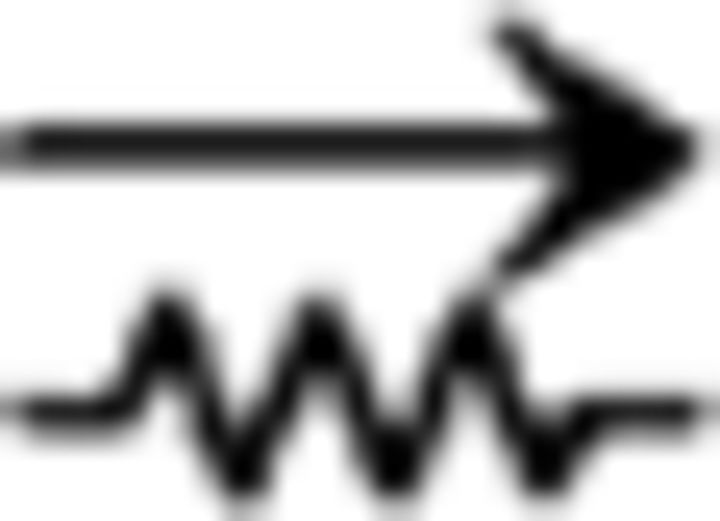 PV: four pairs; PV
PV: four pairs; PV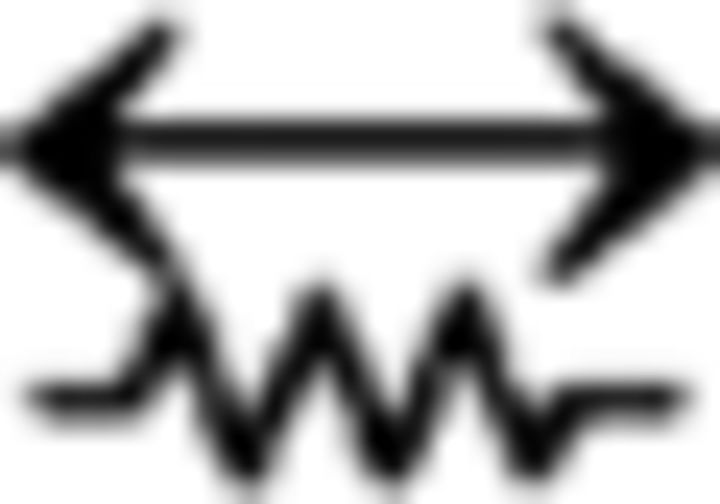 PV: two pairs; unconnected: three pairs. For the vertical axis of the calibration bars in B, E, and F, the top value is for the presynaptic cell and the bottom value is for the postsynaptic response.
PV: two pairs; unconnected: three pairs. For the vertical axis of the calibration bars in B, E, and F, the top value is for the presynaptic cell and the bottom value is for the postsynaptic response.
