Figure 5.
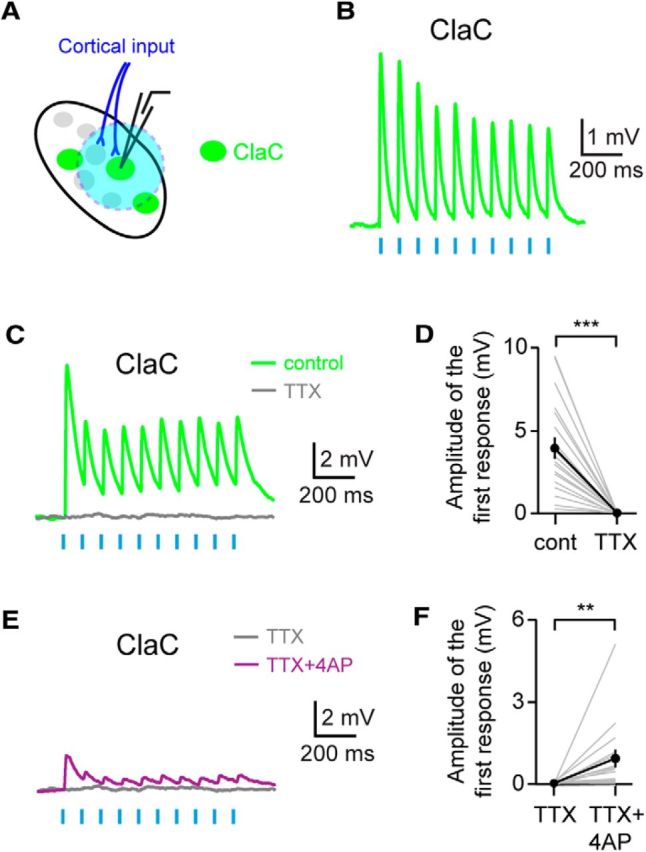
Corticoclaustral axons form monosynaptic connections onto ClaC cells. A, Experimental configuration with corticoclaustral afferents expressing ChR2 (blue) and retrogradely labeled ClaC neurons (green). B, Short-latency responses recorded in a ClaC neuron following optogenetic stimulation of corticoclaustral axons. C, Example recording showing that these short-latency responses are eliminated with bath application of the sodium channel blocker TTX. This is a different neuron from the one shown in B. D, Summary data showing that bath application of TTX eliminated the responses in ClaC neurons following optogenetic activation of corticoclaustral afferents (n = 19, p = 0.000004, sign test). E, Example recording showing that bath application of the potassium channel blocker 4-AP in combination with TTX reveals direct monosynaptic connections between corticoclaustral axons and a ClaC neuron. This recording is from the same ClaC neuron shown in C. F, Summary data showing the monosynaptic responses in ClaC neurons to cortical input following bath application of 4-AP and TTX (n = 16, p = 0.004, sign test).
