Fig. 5.
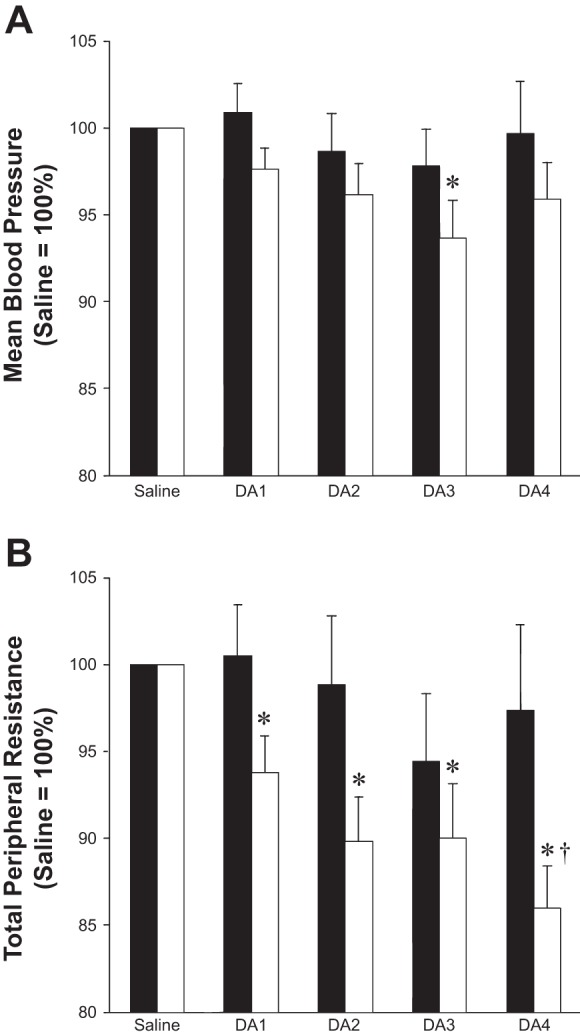
Effect of dopamine dose on steady-state hemodynamics, reported relative to responses during saline infusion (saline = 100%). High HVR (n = 13), low HVR (n = 17). A: a significant reduction in blood pressure was observed in subjects with low baseline chemosensitivity during intravenous dopamine infusion (3 μg·kg−1·min−1) (white bars, P < 0.01). No changes in blood pressure were observed in subjects with high baseline chemosensitivity (black bars, P = 0.59). B: subjects with low baseline chemosensitivity exhibited a significant decrease in total peripheral resistance at each dose of dopamine (P < 0.01) which was not observed in subjects with high baseline chemosensitivity (P = 0.51). *P < 0.05 vs. saline; †P < 0.05 vs. 1 μg·kg−1·min−1. Data are presented as means ± SE.
