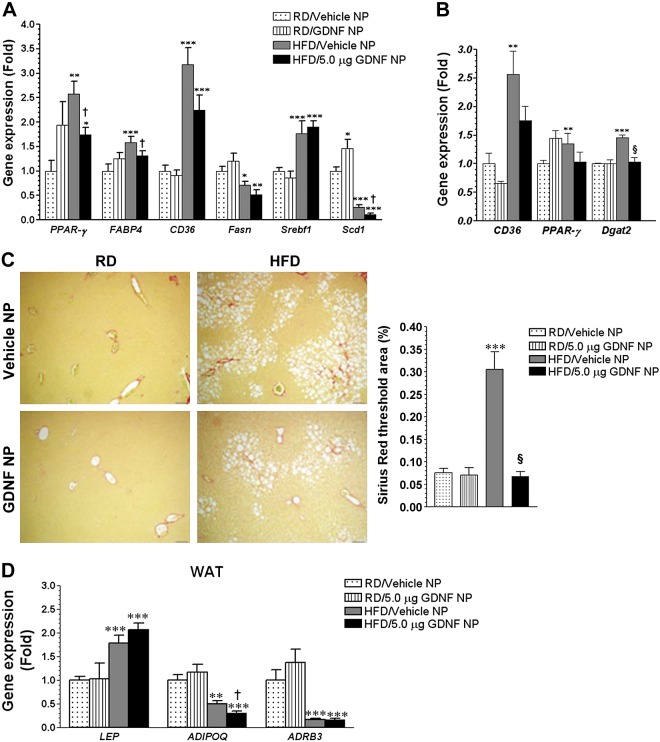
Fig. 6.
GDNF-loaded nanoparticles suppress the expression of steatosis-associated genes in mice with longstanding hepatic steatosis. A: assessment of gene expression in liver from WT mice fed RD or HFD for 16 wk and daily injected with Vehicle NP or GDNF NP during the final 5 wk. Plotted are means + SE. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, and *P < 0.05 relative to mice fed RD and injected with Vehicle NP; †P < 0.05 relative to Vehicle NP-injected, HFD-fed mice. B: analysis of gene expression in liver from WT mice maintained on a RD or HFD for 19 wk and daily injected with Vehicle NP or GDNF NP during the last 13 wk of the study. Plotted are means + SE. ***P < 0.001 and **P < 0.01 relative to mice maintained on the RD and injected with Vehicle NP; §P < 0.001 relative to mice maintained on the HFD and injected with Vehicle NP. C: Sirius Red-stained liver sections from WT mice fed the RD or HFD for 19 wk and daily injected with Vehicle NP or GDNF NP during the last 13 wk of the study, and comparison of staining area. Scale, 50 μm. Plotted are means + SE. ***P < 0.001 relative to mice maintained on the RD and injected daily with Vehicle NP; §P < 0.001 relative to mice maintained on the HFD and injected with Vehicle NP. D: analysis of gene expression in white adipose tissue (WAT) from mice maintained on a RD or HFD for 19 wk and daily injected with Vehicle NP or GDNF NP during the last 13 wk of the study. Plotted are means + SE. ***P < 0.001 and **P < 0.01 relative to mice maintained on the RD and injected with Vehicle NP; †P < 0.05 relative to mice maintained on the HFD and injected with Vehicle NP.