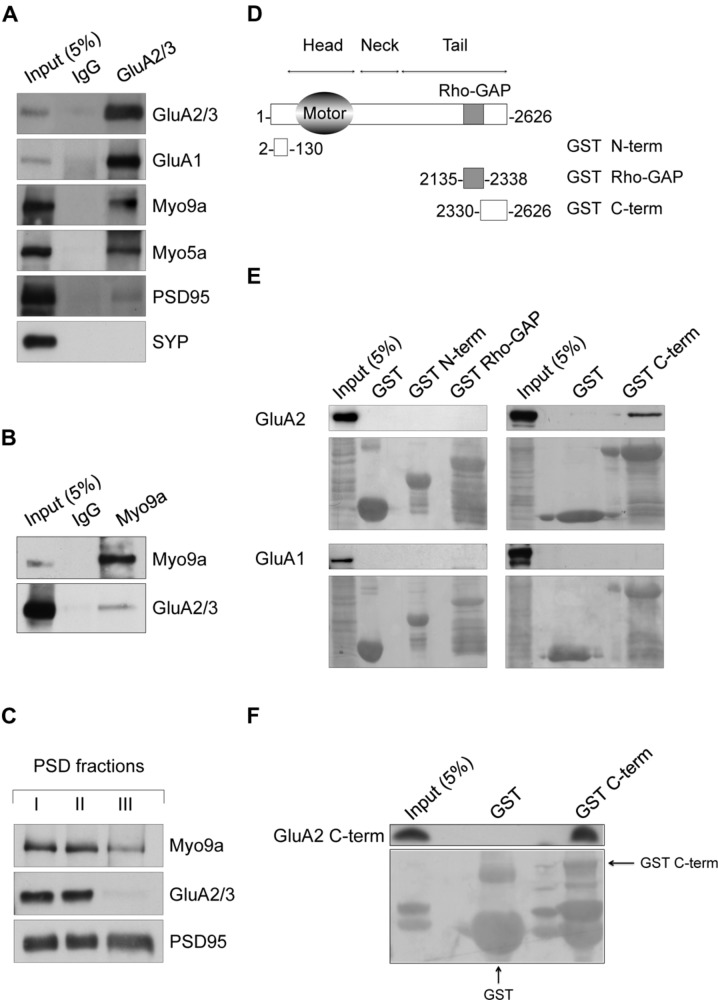
FIGURE 1.
Myosin IXa (Myo9a) localizes at excitatory synapses and binds the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptor (AMPAR) GluA2 subunit. (A) Western blots of co-immunopurified proteins from DIV18 hippocampal neurons using anti-GluA2/3 antibodies or non-immune IgGs as a control. GluA1, Myo9a, Myo5a, and reduced amounts of PSD95 were co-purified with GluA2/3, but SYP was not. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of GluA2/3 with Myo9a from mouse hippocampal homogenates. (C) Biochemical fractionation of Myo9a in rat brain showing the presence of Myo9a in postsynaptic density (PSD) fractions that were extracted with Triton X-100 once (PSD I) and twice (PSD II). Myo9a was reduced following extraction with Triton X-100 followed by sarkosyl (PSD III). (D) Schematic structure of Myo9a and its domains fused to GST. (E) Western blots of pull-down assays from HEK293 cells expressing either GluA2 (top) or GluA1 (bottom) using GST N-term, GST Rho-GAP and GST C-term or GST as a control. Myo9a C-terminal region (GST C-term) binds GluA2 but not GluA1. Note that a blank line was left between each sample line to avoid overflow artifacts. A small amount of overflow into the adjacent wells appears as additional narrow lines. (F) In vitro pull-down assays of purified GluA2 C-terminus (GluA2 C-term) using Myo9a GST C-term, which indicates that Myo9a and GluA2 C-termini directly interact. GST fusion proteins were visualized using Ponceau Red staining (underneath each immunoblot). GST fusion proteins are indicated using arrows. Small amount of overflow into the adjacent wells appear as additional narrow lines.