Fig. 4.
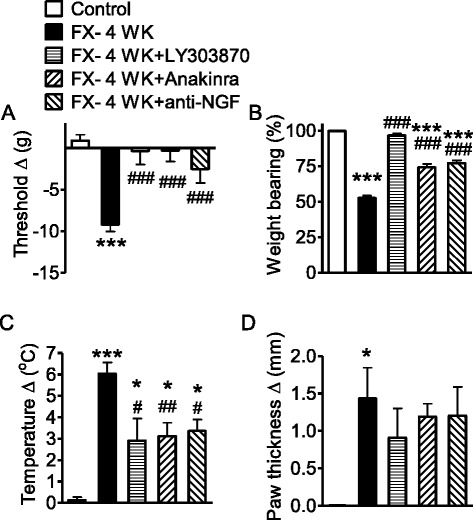
Systemic administration of LY303870, anakinra, and anti-NGF reversed fracture-induced nociceptive and vascular responses at 4 weeks after fracture. LY303870 (30 mg/kg/day i.p.) was administered for 7 days between 3 and 4 weeks post fracture. Anakinra was administered at 10 mg/kg/day s.c. in a pump for 28 days prior to testing at 4 weeks post fracture. Anti-NGF (10 mg/kg s.c.) was administered at 7 days prior to testing at 4 weeks post fracture. a Tibia fracture induced mechanical allodynia to von Frey testing at 4 weeks (control cohort, n = 10; FX- 4 WK, n = 10), and LY303870 (n = 8), anakinra (n = 10), and anti-NGF (n = 10) all reduced this sensitization. b At 4 weeks, unweighting developed in the ipsilateral hindpaw in fracture rats, and again, the test agents reduced the unweighting response. c Warmth was observed in fracture rats at 4 weeks, but fracture rats treated with LY303870, anakinra, or anti-NGF showed reduced temperature differences. d Edema indicated as an increase in hindpaw thickness was found at 4 weeks after fracture. Cohorts of rats treated with each of the test agents failed to show statistically significant changes in edema. Measurements for a, c, and d represent the difference between the fracture ipsilateral side and the contralateral paw. Measurements displayed in b represent weight-bearing on the fracture hindlimb as a ratio to 50 % of bilateral hindlimb loading. Data are expressed as mean values ± standard error (SE) and analyzed to compare fracture at 4 weeks versus non-fracture control cohorts and fracture with treatments versus fracture at 4 weeks cohorts using one-way ANOVA followed by Neuman-Keuls multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, fracture at 4 weeks versus control rats; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, and ### P < 0.001, fracture with treatments versus fracture at 4 weeks (panels b–d, control cohort, n = 6; FX- 4 WK, n = 8; FX- 4 WK + LY303870, n = 8; FX- 4 WK + anakinra, n = 10; FX- 4 WK + anti-NGF, n = 7)
